* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparison of p53 Structure: Wild type vs. mutant
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
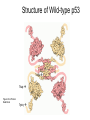
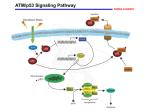
Comparison of p53 Structure: Wild type vs. mutant What change in wild type p53 may lead to cancer? Structure of Wild-type p53 1olg 1tup Figure from Protein Data Bank 1ycq Structural Domains of p53 • • • • • Composed of 4 polypeptide chains Each chain has 3 domains Tetramerization domain named 1olg DNA binding domain named 1tup Activation domain named 1ycg Structure of DNA Binding domain is highly conserved (purple) Figure from ConSurf Same molecule (1tup) as ribbon diagram Figure from ConSurf • Notice that the portion of the protein that directly interacts with the DNA is highly conserved (purple) • Other protein regions are less highly conserved One amino acid substitution from a mutant p53 Figure from ConSurf Protein Alignment of Wild-type p53 vs. mutant p53 • LRVEYLDDRNTFRHSVVVPYEPPEVGSD • LRVEYLDDRNTFRHSVVVPYEPPEVGSE • Summary: Amino acid substitution DE is from aspartate to glutatmate (both are negatively charged) Summary • Mutations involving amino acids substitutions in conserved domains can negatively affect function of p53. Future Work • Identify the specific amino acid locations in the 1tup and determine if the mutations are in the highly conserved region and indicate these on our figures