* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A- The Life Processes
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
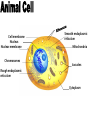
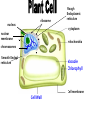
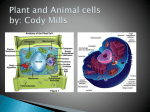
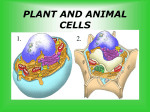
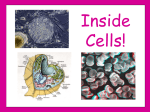
th 7 Grade Science Living Systems Organisms I- Living Things Carry Out Life Processes A- Organisms, (any living thing) share certain characteristics that set them apart from nonliving things. B- Life Processes: 1-Getting and using energy a-Nutrition: Taking in food (ingestion) & down into a usable molecule (digestion). b-Transport: Move materials throughout organism. c-Respiration: Releasing energy stored in food. breaking it 2- Getting rid of wastes: Excretion 3- Respond to changes in the Environment: (Stimulus causes a Response) Regulation 4- Growth & Development: Changing food into more of themselves. 5- Reproduction: Making of more organisms of the survival of the species. same kind to ensure The Cell Basic Unit of Life: 1- Cell Theory: States that all organisms are made of cells or of a cell, all cells come from other cells. 2- Cells Vary: a- size, shape, and arrangement. b- Unicellular: one cell c- Multicellular: many cells. 3- Parts and Function of Animal Cells a- Cell Membrane: thin structure covering the surface of the cell. •Allows materials needed by cell to enter and wastes to leave. b- Cytoplasm: jellylike substance that fills cell. Contains proteins for growth and repair. Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane Chromosomes Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria Vacuoles Rough endoplasmic reticulum Cytoplasm c- Organelles: tiny structures in cytoplasm perform special jobs. that Nucleus: “Control Center” Controls cell activities. These are stored in the chromosomes found in nucleus on genes. Nuclear membrane: allows and leave nucleus. information to enter Mitochondria: “Powerhouse” cell respiration food is burned by combining it with oxygen to release energy. Endoplasmic reticulum: channels that run throughout the cell store and transport materials. Ribosome proteins used for growth and repair. Vacuoles: stores materials. 4-Plant Cells differ from Animal Cells a- Cell Wall: gives support and shape b- Chlorophyll: contains chloroplast for carrying out photosynthesis. c- Large Vacuoles: stores mostly water. nucleus ribosome Rough Endoplasmic reticulum cytoplasm nuclear membrane mitochondria chromosomes Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Chlorophyll Cell membrane Cell Wall 5- Bacteria cells have no nucleus, mitochondria, or endoplasmic reticulum. They still carry out all five life processes. Cell Wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Microorganisms: Are unicellular organisms 1-Harmful Microorganisms: Cause infectious diseases that can be passed on from one organism to the next. a. Noninfectious diseases: Diseases that are not caused by microorganisms. ~High blood pressure, asthma, cancer etc.. ~Causes = poor diet, allergies, chemicals, heredity etc… 2-Helpful Microorganisms: about 5% a. Examples: ~ Decomposers: Break down dead materials and return nutrients back into soil. ~ Yeast: bread, wine, and beer. ~ Mold: Cheese, and medicine A- The Life Processes Getting and Using Energy •Getting ride of wastes •Growth and Development •Responding to Changes in Environment •Reproduction A Closer look at Life Processes: 1-Transport: is the movement of materials through organism. Water is a key nutrient for this to occur. *Two types: Diffusion molecules move from a high concentration to a low concentration with out the use of energy. Osmosis: diffusion of water. Active Transport used by cells need to move molecules from low concentration to a high concentration. Cells require the use of energy. 2- Getting and using energy: a- Nutrition plants: Green plants make own food. Through the processes of photosynthesis * Photosynthesis: plants use energy from the sun and change carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O into sugar C6H12O6. Energy from the sun is therefore stored in sugar. *Photosynthesis produces oxygen O2. *Chlorophyll green pigment in leaves contains chloroplast needed for photosynthesis. b-Nutrition Animals: get energy “nutrition” by eating other plants or animals. The original source of energy is the sun. “Water” is also an important part of nutrition in plants and animals. c- Respiration: is the processes that organisms use to release “burn” energy stored in food. Respiration is the opposite of Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis: energy + carbon dioxide + water = sugar + oxygen Respiration: sugar + oxygen = energy + carbon dioxide + water All organisms get energy directly or indirectly from the SUN 3- Getting ride of wastes : “Excretion” process of removing waste from the body. Filtered out of blood. water. a-Wastes = Carbon dioxide, urea, salt & excess b-Wastes are removed by exhaling, perspiring, and urinating in animals, and by transpiration in plants. 4-Responding to changes in the environment: regulation Organisms changes respond to internal and external in their environment known as Stimuli. a- Examples = migration, drinking, hibernation, growing of fur etc.. perspiring, b- Regulation helps organisms maintain “homeostasis” the maintenance of a constant internal environment. 5-Reproduction: Organisms reproduce survival of species. to ensure the a- Two Types of reproduction: 1) Asexual Reproduction: process of producing a new organism with only one parent. The new organism has the exact same DNA as the parent. b- Types of Asexual Reproduction: Fission or Binary Fission: one cell splits to form two cells with the same DNA Budding: a new organism grow from the body of the parent. The bud can stay on to form a colony, or break apart Regeneration: A new organism forms from a piece of the parent or the parent re-grows the missing piece Sporulation: Some organisms reproductive cells in a Spore. produce protective covering called a 2) Sexual Reproduction involves the combination of DNA from two parents. Fertilization is the joining of DNA from The male (SPERM, POLLEN) and DNA of the female (EGG). The new organisms is a combination of both parents.