* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Transport
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
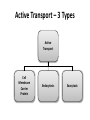
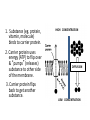
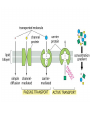
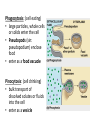
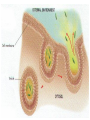
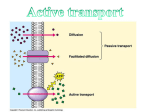
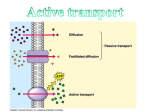
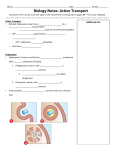
Active Transport pp. 67 to 71 • We know that passive transport involves NO energy, but.... • As living beings, we NEED energy to sustain life processes. We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be sustained inside body as it is soluble, so it must be converted into glycogen to get energy “stores” – This conversion MAKES energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) = source of energy for cells – ATP reacts with certain compounds to release energy to drive life processes Active Transport – 3 Types Active Transport Cell Membrane Carrier Protein Endocytosis Exocytosis 1. CM Carrier Protein • Bit similar to facilitated diffusion, but… • Cell energy (ATP) is used to move substance across CM against concentration gradient (low high) – Remember, simple diffusion is the movement of substances using no energy to maintain equal concentrations on both sides (high low = equal) 1. Substance (eg. protein, vitamin, molecule) binds to carrier protein. 2. Carrier protein uses energy (ATP) to flip over & “pumps” (releases) substance to other side of the membrane. 3. Carrier protein flips back to get another substance. HIGH CONCENTRATION DIFFUSION LOW CONCENTRATION Bulk Transport • Diffusion and CM carrier proteins move small amounts of molecules, sometimes ONE molecule at a time. It works but may not be the most efficient. • Cells need to move large amounts of materials (bulk) in or out of the cell, all at once = bulk transport • Involves energy (ATP) • Two kinds of bulk transport: endocytosis and exocytosis 2. Endocytosis • A type of bulk transport that is used to bring large amounts of material INTO the cell. • There are 2 kinds: – Phagocytotis: bulk transport of solids – Pinocytosis: bulk transport of liquids Phagocytosis: (cell eating) • large particles, whole cells or solids enter the cell • Pseudopods (sin: pseudopodium) enclose food • enter as a food vacuole Pinocytosis: (cell drinking) • bulk transport of dissolved solutes or fluids into the cell • enter as a vesicle Exocytosis • A type of bulk transport that is move large amounts of material OUT of the cell. • Materials are encased in secretory vesicles (in case of proteins, vesicles form at the end of the Golgi appartus and breaks off) • The vesicle move towards CM. Vesicle fuses with CM and expels content to extracellular fluids.