* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Manipulatives/Review Activity [Characteristics of the 6 Kingdoms]
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
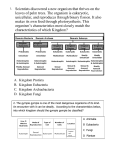
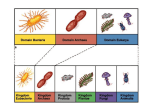
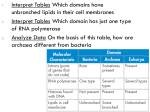
Manipulatives/Review Activity [Characteristics of the 6 Kingdoms] Organisms are classified into kingdoms based on cell structure, ability to make food, and number of cells. 6 There are _______ kingdoms of organisms. They are… Mushrooms, yeast Fungi • • • • • • Eukaryote Cell walls made of chitin Most are multicellular (yeast is unicellular) Heterotroph No movement Asexual or sexual reproduction Sponges, coral Animalia • • • • • • Eukaryote No cell walls Multicellular Heterotroph Moves Sexual reproduction Escherichia coli Eubacteria • Prokaryote • • • • • Cell walls with peptidoglycan Unicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Can move with flagella Asexual reproduction Plantae • Eukaryote • Cell walls made of cellulose, contains chlorophasts • Multicellular • Autotroph • No movement • Sexual reproduction Some found in extreme environments, like acidic drainage and hot springs: Archaebacteria • Prokaryote • Cell walls without peptidoglycan • • • • Unicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Can move with flagella Asexual reproduction Protista • Eukaryote • Cell walls with cellulose; Some have chloroplast • Most are unicellular • Autotroph or Heterotroph • Can move with flagella or cilia • Asexual or sexual reproduction This cell is … a. prokaryotic b. eukaryotic Place your kingdom cards into two groups • Eubacteria • Archaebacteria • • • • Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia The leaves on the tree are green because they contain chloroplasts that enable them to photosynthesize. Therefore the tree is a(n) a.Heterotroph b.Autotroph Now, place your kingdom cards into two groups • • • • Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Plantae • • • • • Eubacteria Archeabacteria Fungi Animalia Protista This organism is said to be unicellular. Now, place your kingdom cards into two groups • • • • Protista (some) Plantae Anamalia Fungi • • • • Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi (yeast only) The cell shown here is a plant cell. How do we know? One way is by the presence of the cell wall. Which of your cards fit into these two categories? • • • • • Eubacteria Archeabacteria Protista (some) Fungi Plantae • Animalia • Protist Homework Q. 1 What is the main difference between the Eubacteria and the Archaebacteria? Archaebacteria does not have peptidoglycan and can live in extreme enviroments Homework Q. 2 If you know an organism has a cell wall and is a multicellular autotroph, can you determine the kingdom to which it belongs? Homework Q. 3 If you know an organism is unicellular, has a nucleus and can make its own food, can you determine the kingdom to which it belongs? Now, Let’s see how much you learned! Put your worksheet somewhere that you cannot see it. Open envelope 2! In your envelope are cards that have pictures, diagrams or characteristics of organisms. Line up your kingdom cards on the left (similar to below) and then sort your other cards into the correct kingdoms. Archaebacteria Plantae Animalia Protista Eubacteria Fungi Assessment • From the information on the following slides, determine the kingdom that is represented. 1. Multicellular eukaryotes that are usually mobile and obtain food from other organisms. 2. A researcher examined prepared slides of pond water. Single-celled organisms with a nucleus and either cilia or flagella were visible. 3. 4. Some Characteristics of Diospyros texana • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • Makes its own food 5.