* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. diffusion - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
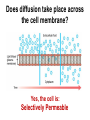
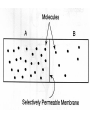
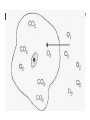
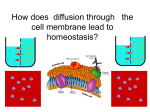
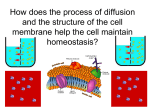
AIM: How does the process of diffusion and the structure of the cell membrane help the cell maintain homeostasis? DN: Can all substances move through the cell membrane? What determines what substances are able to move through the cell membrane? Give an example of a substance that can move through the cell membrane and an example of a substance that cannot move through the cell membrane. HW: Page 198-199 #15,16,26,27 What is diffusion? The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. What do we mean when we say concentration? The amount of a particular substance The reason diffusion occurs is because molecules are always… MOVING What is the end result of diffusion? The number of particles are now evenly distributed This is called: Dynamic Equilibrium Dynamic Equilibrium At this point, the number of particles have spread themselves out equally throughout the beaker. Are the particles still moving after dynamic equilibrium has been reached? YES An illustration of diffusion: Two Conditions for Diffusion: 1) concentration gradient 2) no barrier blocking the movement of particles. What is a concentration gradient? The difference in concentration between a region of high concentration and a region of lower concentration. What do we mean by a barrier? Will diffusion take place? YES Will diffusion take place now? NO The particles must be free to move down their concentration gradient in order for diffusion to occur. Does diffusion take place across the cell membrane? Yes, the cell is: Selectively Permeable Cell Membranes are: Selectively Permeable A selectively permeable membrane allows some substances to cross the membrane more easily than others and blocks the passage of other substances altogether. Cell Membranes help organisms maintain HOMEOSTASIS By controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. To stay alive, a cell must exchange materials such as food, water, and wastes with its environment. What is the main job of the cell membrane? HOMEOSTASIS & TRANSPORT • Cell membranes helps organisms maintain _____________ by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells • To stay alive, a cell must exchange materials such as food, water, & wastes with its environment