* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diatoms
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
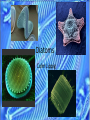
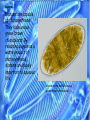
Diatoms Colm Lippig Diatoms Diatoms are a major type of algae/plankton. Most are unicellular although they have been known to grow in colonies of different shapes and sizes like spirals. Most diatoms are motile. A diatom colony living alongside other algae Diatoms Diatoms grow hydrated silica “shells” to protect themselves from harm. These cell walls often form in two pieces that fit together like a box and a lid. There is a wide diversity in how they look. Tiny pores in the silica allow for gas exchange Different types of diatoms Diatoms Most of the time, diatoms reproduce asexually by mitotic cell divisions. Each daughter cell receives half the cell wall of the original diatom and then regenerates the other half. They also reproduce sexually. The regeneration of the second piece of the cell wall causes a unique shrinking effect Diatoms Diatoms are capable of photosynthesis. They have unique green-brown chloroplasts. By releasing oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis, diatoms are hugely important to aqueous life. Most diatoms exhibit unique green-brown chloroplasts General video on Diatoms: A murder conviction is based on diatoms: http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=aNM3AfGPHfw &NR=1 http://www.pbs.org/wn et/nature/episodes/cri me-scenecreatures/video-diatomdetective/5208/ Review Questions 1. What type of protists are diatoms? 2. What unique color do the chloroplasts of most diatoms share? 3. True or false, diatoms can be found in both fresh and salt water. 4. The asexual division of diatoms leaves each daughter with how much of the cell wall? 5. The cell walls of diatoms are made of what material? 6. Although diatoms are unicellular, they have been known to form what?