* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Boundaries
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
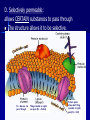
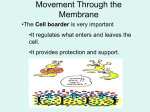
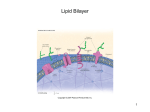
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries Part 1 (of 4)Notes I. Cell Membranes: ALL cells have one! A. Outer boundary of the cell B. Functions 1) Separates a cell from other cells 2) Protection and support 3) Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain homeostasis C. Structure: MOSTLY A LIPID BILAYER, with proteins and carbs scattered throughout. 1) 2 layers of phospholipids a) polar head: forms outsides (bread) of bilayer Described as hydrophilic: water loving, attracts water b) non-polar tail: forms inside (PB&J) of bilayer Described as hydrophobic: water fearing, avoids water (polar)HEAD Hydrophilic (nonpolar) TAIL Hydrophobic 2) Proteins with carbohydrate chains are wedged between Phospholipid molecules. a) Proteins act as pores, channels or pumps to move substances into or out of cell. b) Carbohydrates are markers which are used for cell identification. D. Selectively permeable: allows CERTAIN substances to pass through The structure allows it to be selective. Ex. Glucose can pass through Things soluble in Lipids can pass (Ex. Alcohol) Protein pores allow small thing insoluble in lipids pass( Ex. H20) – Molecules can pass through IF : – They are soluble in lipids, they can easily pass through bilayer (ex. Alcohol, CO2, O2, steroids) – If they are NOT soluble in lipids (water, gulcose amino acids, ions: May be small enough to get through protein pores (ex. water) May be able to go through a protein channel (ex. Glucose) May be able to get pushed through by a protein pump Ex. Na+(sodium ion), K+(potassium ion) Examples of substances that need to pass into cell: – 1. water 2. glucose 3.oxygen Examples of substances that need to pass out of cell: – 1. carbon dioxide 2. water II. Cell Walls A. Found in: 1) Plants 2) Algae 3) Bacteria 4) Fungi (Have both cell membrane AND cell wall) B. NOT IN ANIMAL CELLS C. Function: EXTRA Support and protection, and gives extra strength to cells D. Composed of fibers of carbohydrates: Plants 1. Cellulose in _____________ 2. Chitin in _______________ Fungi Eubacteria 3. Peptidoglycan in ___________________ REVIEW QUESTIONS How does water move through the cell membrane? _______________ Through PROTEIN pores What does semi-permeable mean? Only allows certain substance through ___________________________________ Phospholipid What molecule is the lipid bilayer made of? ___________ Head tail Which part is polar? _______Which is nonpolar?_________ How does one cell recognize that a cell is part of that tissue or organ? _____________ Carbohydrate chain What is a substance that is soluble in lipids, that would pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane Alcohol easily?_______ False –animal cells don’t True or False: All cells have cell walls? ______________ In Da Club - Membranes & Transport: Crash Course Biology #5 - YouTube