* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life is Cellular
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
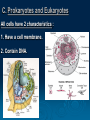
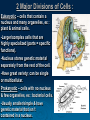
Chapter 7: Cell Structure & Function I. Life is Cellular A. The Discovery of the Cell Famous Scientists & the Cell Theory : 1. Robert Hooke – (1665) English scientist who used an early compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork. -1st used the word “cell”, referring to tiny, empty chambers that make up plant cork. 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Dutch scientist who used a single-lens microscope to view pond water & other things. Was a lens-maker. Famous Scientists & the Cell Theory 3. Matthias Schleiden – (1838) German botanist who 1st concluded that all plants are made of cells. 4. Theodor Schwann – (1839) German biologist who 1st concluded that all animals are made up of cells. -Said all living things are made of cells. 5. Rudolf Virchow – (1855) German physician who concluded that new cells only come from existing cells. Famous Scientists & the Cell Theory *Work done by these scientists led to the development of the cell theory. The cell theory states : 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. B. Exploring the Cell *New techniques & microscopes are now used to explore the cell closely. Techniques : 1. Fluorescent labeling – follows molecules moving through a cell. 2. Confocal light microscopy – scans cells w/ laser beam; used to build 3-D images of cells & cell parts. 3. High-resolution video technology - produces movies of cells as they grow, divide, & develop. Types of Electron Microscopes 1. TEMs – (transmission electron microscopes) used to study cell structures & protein molecules. 2. SEMs – (scanning electron microscopes) scan surfaces of specimens & make 3-D images. 3. Scanning probe microscopes – trace surfaces of samples with a fine probe. Great for surfaces; can view single atoms. C. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes All cells have 2 characteristics : 1. Have a cell membrane. 2. Contain DNA. 2 Major Divisions of Cells : Eukaryotic – cells that contain a nucleus and many organelles, ex : plant & animal cells. -Larger/complex cells that are highly specialized (parts = specific functions). -Nucleus stores genetic material separately from the rest of the cell. -Have great variety; can be single or multicellular. Prokaryotic – cells with no nucleus & few organelles, ex : bacterial cells. -Usually smaller/simple & have genetic material that isn’t contained in a nucleus.