* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
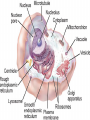
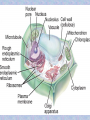
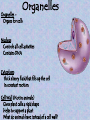
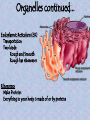
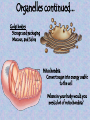
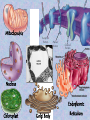
Chapter 7 "Little eels, or worms, lying all huddled up together and wriggily, and the whole water seemed to be alive with these animalcules filled with juices." -- Anton van Leeuwenhoek's observations of a drop of pond water, as he stared through the eyepiece of his newly built microscope in 1673 Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Prokaryote – Bacteria no membrane-bound organelles plasma membrane Eukaryote – Found in plants, animals, fungus, and protists (everything except bacteria) Membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus that contains DNA The Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Membrane – regulates transport of materials (nutrients in & waste out) made of lipids (fat) Selective permeability – controls how much comes in or out based on the cells needs Water Loving Water Hating Three types of proteins are found in the cell membrane 1. Channel proteins let stuff in and out of the cell (transport of materials) 2. Receptor proteins – transfer information to the cell about its surroundings 3. Marker proteins – (organ transplants) name tags for cells allowing them to recognize each other Fluid Membrane Receptor Protein Marker Protein Channel Protein Organelles – Organs for cells Nucleus Controls all cell activities Contains DNA Cytoplasm thick slimey fluid that fills up the cell In constant motion See cytoplasmic streaming Cell Wall (Not in animals) Gives plant cells a rigid shape Helps to support a plant What do animals have instead of a cell wall? Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Transportation Two kinds: Rough and Smooth Rough has ribosomes Ribosomes Make Proteins Everything in your body is made of or by proteins Golgi bodies Storage and packaging Mucous, and Saliva Mitochondria Convert sugar into energy usable to the cell Where in your body would you need a lot of mitochondria? Chloroplasts Contain chlorophyll Make food from sunlight Vacuoles Storage (for food and water) What cells might have bigger vacuoles? Plant cells have big vacoules why??? Movement • Cilia – Short projections that look like hair – Can be used for movement or to absorb • Flagella – Longer and less in # – Create movement with whiplike motion Mitochondria Receptor Protein Marker Protein Channel Protein Nucleus Endoplasmic Chloroplast Golgi Body Reticulum