* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
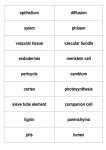
Transport in Plants Spot the Difference! Transport in Plants • Xylem water and soluble minerals travel upwards • Phloem sugars travel up and down Section of a Plant Root xylem phloem • Xylem cells arranged in a cross shape • Phloem cells within the corners of the xylem Section of a Leaf • Vascular bundles form the midrib and veins of the leaf • Xylem above phloem Section of a Stem Vascular bundle xylem phloem cambium (in between the xylem and phloem) • Separate vascular bundles • Bundles towards outer edge of stem • Ring of vascular tissue around the edge of stem • Xylem towards inside and phloem towards outside of stem • Cambium - layer of meristem cells. Undifferentiated. Produce new xylem and phloem phloem phloem xylem cambium Function of Xylem • Transports water and minerals from roots to the rest of plant • Transported upwards Structure of Xylem • Tubes to carry water and dissolved minerals, fibres for support • Xylem vessel elements (living parenchyma cells) impregnated by lignin • Lignin waterproofs the cell walls and prevents them from collapsing. This leaves a long column of dead cells • Water can pass through the cell walls through pits • No cell contents, nucleus or cytoplasm Function of Phloem • Transports sugars from one part of plant to another • Transported up or down 2 types of cell – sieve tube elements – companion cells Linked by plasmodesmata Structure of Phloem Sieve tube element • Very little cytoplasm, no nucleus • Lined end to end forming a tube • Contains perforated cross-walls (sieve plates) – allows sap through the pores Companion cell • Large nucleus, dense cytoplasm, many mitochondria • Responsible for metabolic processes (requires ATP)