* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Xylem and phloem as part of the vascular bundle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
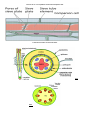
Xylem and phloem as part of the vascular bundle in a stem Cambium lies in the middle as undifferentiated tissue and so can form new xylem vessels and phloem tubes at the same time Xylem and phloem compared Phloem Xylem Movement: Bidirectional Unidirectional (upward) Function: Transportation of food and nutrients from leaves to storage organs and growing parts of plant. Water and mineral transport from roots to aerial parts of the plant. Structure: Tubular with soft walled cells Tubular with hard walled cells Occurrence: Roots, stems and leaves Roots, stems and leaves Additional Functions: Forms vascular bundles with xylem Forms vascular bundles with phloem and gives mechanical strength to plant due to presence of lignified cells. Elements: Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, bast fibers, intermediary cells Tracheids, vessel elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem sclerenchyma Nature of tissue: Living tissue Non living tissue at maturity Picture of a L.S. of a phloem vessel and companion cell Transverse section of root and stems Root Stem