* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Individuals DON`T evolve…
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
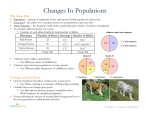
Individuals survive orevolve… don’t survive… Individuals DON’T Populations evolve Individuals reproduce or don’t… Individuals are selected Populations evolve! Definition of evolution: change in the allele frequency in a population over time. 5 Agents of evolutionary change Mutation Gene Flow Genetic Drift Non-random mating Selection Gene Pool • The sum total of all the genes present in a population at any one time. AA AA aa AA Aa aa Aa • The state of the gene pool will indicate if the population is stable or undergoing evolutionary change. aa Aa AA AA aa Aa AA A gene pool made up of 16 individuals Aa Gene Pool Geographic boundary of the gene pool Individual is homozygous recessive (aa) AA Aa AA AA aa Aa Aa Individual is homozygous dominant (AA) aa aa AA Aa aa Aa Aa AA AA Individual is heterozygous (Aa) A gene pool made up of 16 individual organisms with gene A, and where gene A has two alleles Analyzing a Gene Pool • By determining the frequency of allele types (e.g. A and a) and genotypes (e.g. AA, Aa, and aa) it is possible to determine the state of the gene pool. Stable allele frequencies over time indicates no evolution Changing allele frequencies over time indicates evolution is occurring Aa Aa AA aa Aa AA Aa Aa aa Determining Allele Frequencies • To determine the frequencies of alleles in the population, count up the numbers of dominant and recessive alleles, regardless of the combinations in which they occur. Aa AA aa Aa AA Aa No. of dominant alleles Aa Total no. of alleles Aa Determining Genotype Frequencies • To determine the frequencies of different genotypes in the population, count up the actual number of each genotype in the population and divide by the total number of individuals: homozygous dominant (AA) heterozygous (Aa) homozygous recessive (aa). Aa AA aa Aa AA Aa Aa Aa