* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Detection of different genes heredity
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
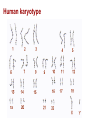
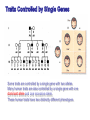
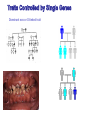
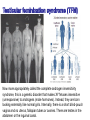
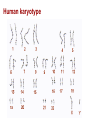
Human karyotype Family history Geneology in animal breeding The goal: Detection of different genes heredity (animals with necessary traits) Geneological method in human genetic The goal: detection of gene heredity Some traits are controlled by a single gene with two alleles. Many human traits are also controlled by a single gene with one dominant allele and one recessive allele. These human traits have two distinctly different phenotypes. E10/I10 tau mutations. RNA sequences for part of E10 (A) and the E10/I10 junction (B) are shown Tau mutation, Parkinson's disease ahondroplasia 1:15 000 līdz 40 000 Polydactyly 4. chromosome Dominant sex or X-linked trait and schematic representation of the sickle gene codominant genes Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell trait is co-dominant with the normal allele and most common in people of African ancestry. Consanguineus marriage in Turkey 25% Son: All family has consanguineous marriages, why I can’t ! Mother: Because we learnt our lesson! There is many children with Abnormalities, you are lucky! Sami, say something to your son! Father: Are you crazy my son? What will you do if you marry with your uncle…. Prof. F. Silan, Turkey, 2015 USA - 1 from 3 000 white-skinned 1 no 17 000 dark-skinned. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder in which the body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and intestines. Bacteria grow in the mucus and can cause infections which can cause lung damage. The mucus also makes it difficult for digestion to occur. most common among people whose ancestors are from Northern Europe. Great Britain 1 from 377 Asians 1 uz 90 000 CF is autosomal recessive inherited. It is known that all (more than 400) gene mutation that causes CF syndrome occurs in 7. chromosome. CF gene, ensure the protein formation consisting of 1 480 amino acids Is called CF transmembrane Regulators (CFTR). Now more appropriately called the complete androgen insensitivity syndrome, this is a genetic disorder that makes XY fetuses insensitive (unresponsive) to androgens (male hormones). Instead, they are born looking externally like normal girls. Internally, there is a short blind-pouch vagina and no uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries. There are testes in the abdomen or the inguinal canal. Human karyotype 11 14 8 7 6 2 18 2 13 15 19 21 16 13 11 3 1 10 20 15 4 17 5 10 18 7 6 14 22 1 X 19 12 17 4 12 3 20 9 5 21 8 Y 9 RISK OF HAVING A LIVEBORN CHILD WITH A CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY