* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis Is a Major Function of Cells
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
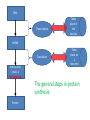
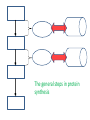
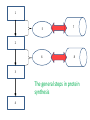
Protein Synthesis Is a Major Function of Cells 4-1 DNA Transcription Takes place in the nucleus mRNA Translation Amino Acid chain, a Takes place on a ribosome Polypeptide The general steps in protein synthesis Protein Figure 4.7 Function of ribosomes Transcription Translation 4-3 1. Transcription is the process of copying the DNA sequence of a gene into a mRNA transcript • Takes place in the nucleus 2. Translation is the process of copying the mRNA transcript into a sequence of amino acids which will eventually become a protein • The mRNA than moves to a ribosome, either attached or free • Free ribosomes are found in the cell’s cytoplasm • Produces proteins for use within the cell • Attached ribosomes are found on the endoplasmic reticulum • Produces proteins for use in the cell membrane or is exported outside of the cell The pathway for proteins being used for the cell membrane or for export out of the cell 1. Nucleus → site of transcription: DNA → mRNA 2. mRNA travels to a ribosome on the endoplasmic reticulum: RER 3. RER → site of translation: mRNA → amino acid sequence: a polypeptide 4. The polypeptide then travels through the RER into the Smooth ER and then to the Golgi body 5. The polypeptide is modified by the SER and Golgi body 6. A vesicle forms on the outside of the Golgi body and then pinches off 7. The vesicle moves through the cytoplasm and fuses with the cell membrane Figure 4.9 Golgi apparatus (graygreen) and transport vesicles 4-6 Figure 4.14 The organelles of the endomembrane system 4-7 The general steps in protein synthesis 1 5 7 2 6 8 3 The general steps in protein synthesis 4