* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell-to-Cell Communication
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
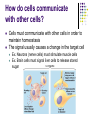
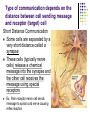
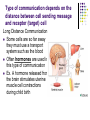
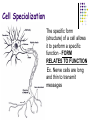
Cell-to-Cell Communication How do cells communicate with other cells? Cells must communicate with other cells in order to maintain homeostasis The signal usually causes a change in the target cell Ex. Neurons (nerve cells) must stimulate muscle cells Ex. Brain cells must signal liver cells to release stored sugar Type of communication depends on the distance between cell sending message and receptor (target) cell Short Distance Communication Some cells are physically connected to each other at junctions. This allows one cell to send a chemical or electrical message directly to the next cell Ex. One heart cell uses an electrical impulse to stimulate neighboring heart cell to contract Type of communication depends on the distance between cell sending message and receptor (target) cell Short Distance Communication Some cells are separated by a very short distance called a synapse These cells (typically nerve cells) release a chemical message into the synapse and the other cell receives the message using special receptors Ex. Pain receptor nerve cell sends message to spinal cord nerve causing reflex reaction Fill It In … Drawing of … Cell Junction Synapse Type of communication depends on the distance between cell sending message and receptor (target) cell Long Distance Communication Some cells are so far away they must use a transport system such as the blood Often hormones are used in this type of communication Ex. A hormone released from the brain stimulates uterine muscle cell contractions during child birth Type of communication depends on the distance between cell sending message and receptor (target) cell Long Distance Communication When long-distance communication is used, the signal must be specifically shaped so that only the target cell will receive the signal. This involves the shape of the hormone and the shape of cell membrane proteins QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Cell Specialization Different cells have different specialized structures and different specialized functions. The specialized function of the cell depends on the unique environment of the cell. Ex. Fresh water vs. salt water environments Fill It In … Long distance cell communication uses __________________ to affect ________________ cells. Cell Specialization The specific form (structure) of a cell allows it to perform a specific function - FORM RELATES TO FUNCTION Ex. Nerve cells are long and thin to transmit messages Fill It In … Drawing of a nerve cell: Check Yourself! 1. Name two ways cells that are close to each other communicate. 2. What is the function of a hormone? Check Yourself! 1. Name two ways cells that are close to each other communicate. CELL JUNCTION & SYNAPSE 2. What is the function of a hormone? Check Yourself! 1. Name two ways cells that are close to each other communicate. CELL JUNCTION & SYNAPSE 2. What is the function of a hormone? LONG DISTANCE CELL COMMUNICATION