* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GENES
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Exome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
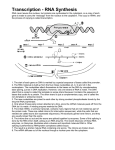
By: Nick Belsanti and Kevin Kukla Translation The DNA of a cell makes mRNA which travels to the ribosome where it reads the sequence of the ribosome and then produces the protein by making amino acids that combine. Translation Amino acids are put into the ribosome by the tRNA and three letters at a time it is translated onto the mRNA until it forms the ribosome. This entire process is called TRANSLATION. Other times the ribosomes embed themselves into the Endoplasmic Reticulum and the protein chains coil within the E.R. this process helps make the Golgi apparatus. Transcription In transcription of DNA, transcription factors are assembled at a specific place on the DNA, an RNA polymerase attaches to these factors it is referred to a transcription initiation complex, Transcription activator proteins start the complex which travels down the double helix of DNA dividing it and copying one strand to form a template for synthesis of an RNA molecule. the 3’ untranslated region is the section of the mRNA where the coding sequence stops the 5’ untranslated region is located just before the mRNA coding sequence. These sequences help regulate the protein synthesis making them critical steps Exons and Introns Non coding DNA is transcribed into functional non coding RNA molecules like mRNA and tRNA. Exons in RNA are the sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA, Introns are RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. Exons and Introns Splicing is the process when an RNA molecule (after transcription)in which the introns are removed and the exons are joined. in coding segments exons are part of the 1.5% coding DNA, in non coding segments introns are part of the 98.5% non coding DNA. Exome and Introme What is an exome?- The exome consists of all the genome’s exons, which are the regions that get translated as proteins. What is an introme? – The introme consists of the introns, which are segments of DNA not needed to code for a protein. Exome GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Study) Exome Sequences Variants; mutations; diseases Issues? Intron What are introns Purposes Genome “Junk” MicroRNA “Gene with a gene” MirTRON http://www.broadinstitute.org/blog/what-exome- sequencing http://www.broadinstitute.org/news/2706 http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2012-11/asoh- sff103012.php http://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/intronintrons-67 http://www.exiqon.com/what-are-microRNAs http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/728457 The END