* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
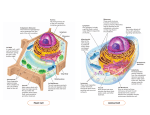
Basic Structure of a Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Nucleolus 1 The cell is the Basic Unit of Life • Cell is the smallest unit of living organisms • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions – e.g. mesophyll cells for photosynthesis and root hair cells for water absorption 2 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 3 BACTERIA CELL copyright cmassengale 4 ANIMAL CELL Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Nucleolus 5 PLANT CELL 6 REVIEW…….. Organisms may be: • Unicellular – composed of one cell • Multicellularcomposed of many cells that may organize 7 REVIEW CONTINUED….. Prokaryotes include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membranebound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) 8 Two Main Types of Eukaryotic Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell 9 Organelles Very small size Can only be observed under a microscope Have specific functions Found throughout cytoplasm copyright cmassengale 10 Cell Membrane 11 Cell Membrane •Protective layer that covers the cell’s surface & controls materials going into and out of the cell •Found in ALL cells •Selectively permeable – “selects” the materials that can permeate (pass through) into the cell 12 CELL WALL 13 CELL WALL • Rigid structure that gives support to the cell – Found in bacteria, plant & fungi cells (NOT in animal cells) – Outermost layer (covers the cell membrane) – Made of cellulose in plant cells & chitin in fungi 14 CYTOPLASM 15 CYTOPLASM Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane 16 NUCLEUS 17 NUCLEUS Large structure found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that controls the activities of the cell Contains the cell’s DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) Genetic material that carries information needed to make new cells and new organisms. Passed from parent cells to new cells 18 Nucleolus found in the middle of the nucleus Makes ribosomes that make proteins copyright cmassengale 19 Golgi Bodies copyright cmassengale Golgi Bodies • Stacks of flattened sacs • Have a shipping side & a receiving side • Receive & modify proteins made by ER copyright cmassengale 21 Endoplasmic Reticulum 22 Endoplasmic Reticulum System of tubes and passageways that are part of the cell’s internal delivery system -found near the nucleus; transports proteins 23 Smooth & Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER lacks ribosomes & makes proteins USED In the cell Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface & makes proteins to EXPORT 24 VACUOLE 25 VACUOLE Storage of water, food & wastes Large central vacuole in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells 26 MITOCHONDRIA 27 MITOCHONDRIA: Produces energy for the cell (ATP) “Mighty mitochondria” Breaks down sugar to release energy through a process called cellular respiration 28 CHLOROPLAST 29 CHLOROPLAST Contain the green pigment chlorophyll Traps sunlight to make to make sugars (food) Process called photosynthesis 30 RIBOSOMES copyright cmassengale 31 RIBOSOMES •Ribosomes – small, grain-like organelles that make proteins –Smallest of all the organelles –Found in ALL cells –Found floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum copyright cmassengale 32 Lysosome 33 Lysosome • Contain digestive enzymes • Break down food and worn out cell parts for cells and help get rid of waste materials • break down & recycle cell parts) 34 Different kinds of animal cells white blood cell Amoeba red blood cell muscle cell cheek cells sperm nerve cell Paramecium 35 Similarities between plant cells and animal cells Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm Both have a nucleus Both contain mitochondria 36 Differences between plant cells and animal cells Animal cells Plant cells Relatively smaller in size Relatively larger in size Irregular shape Regular shape No cell wall Cell wall present 37 Differences between Plant Cells and Animal Cells Animal cells Plant cells Vacuole small or absent Large central vacuole Glycogen as food storage Starch as food storage Nucleus at the center Nucleus near cell wall 38 Levels of organization • Cells are grouped together and work as a whole to perform special functions 39 Tissue • A group of similar cells to perform a particular function – Animals : epithelial tissue, muscular tissue – Plants : vascular tissue, mesophyll 40 Organ • Different tissues group together to carry out specialized functions – Heart : consists of muscles, nervous tissue and blood vessels – Leaf : consists of epidermis, mesophyll and vascular tissue 41 The Structures of a Leaf (Plant Organ) Chloroplast Palisade Mesophyll Cell Spongy Mesophyll Cell Air Space Stoma 42 The Structures of a Heart (Animal Organ) 43 System • Several organs and tissues work together to carry out a particular set of functions in a co-ordinated way – Human : digestive, respiratory, excretory, circulatory and reproductive systems – Plant : root and shoot systems 44 Human Body Systems Examples of systems : Digestive System Respiratory System Circulatory System Nervous System Reproductive System 45 Examples of a Human Body System 46 Examples of a Human Body System The Respiratory System 47 Examples of a Human Body System Circulatory System 48 Examples of a Human Body System Nervous System 49 Levels of Organization CELLS (muscle cells,nerve cells) TISSUES (muscle, epithelium) ORGANS (heart, lungs, stomach) SYSTEMS (circulatory system) ORGANISM (human) 50 It’s You! 51