* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TRANSFORMATION
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
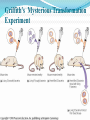
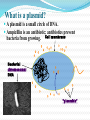
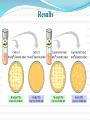
What is Transformation? When a cell takes up and expresses a new piece of genetic material—DNA— in order to change the organism’s traits A gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (coding for) a particular protein One of the three processes(other being conjugation and transduction) by which exogenous materials may be introduced into a bacteria DNA Protein Trait Griffith’s Mysterious Transformation Experiment Frederick Griffiths studied the R & S strains by injecting them into mice S injected into mice -> pneumonia -> death R injected into mice -> harmless Also, boiled S injected into mice -> harmless (bacteria killed by boiling) Griffiths did a strange experiment and got a strange result: Boiled S + live R injected into mice -> pneumonia -> death This was not expected because boiled S and live R were harmless by themselves Took blood samples and found live S in the dead mice Concluded that some factor, a "transforming principle", from the dead S had converted some R bacteria into S bacteria (a genetic change) E. coli Escherichia coli is the most common bacterium in the human gut. It has been extensively studied in the laboratory and is an important research organism for molecular biology. E. coli reproduce very rapidly; a single microscopic cell can divide to form a visible colony with millions of cells overnight. Like all bacteria, E. coli has no nuclear envelope surrounding the bacterial chromosome and thus no true nucleus. All of the genes required for basic survival and reproduction are found in the single chromosome. Types Of Transformation (Natural) its a bacterial adaptation for DNA transfer , depends on expression of numerous bacterial genes. bacteria must become COMPETENT, a special physiological state Limited to about 67 prokaryotic species(7 diff phyla) As an adaption for DNA repair Transformation is induced in Streptococcus pneumoniae by DNA damaging agents mitomycin C(crosslinking agent) and fluroquinole(breaks double bonds) Natural Competence 1% of bacteria is naturally capable of competence under lab conditions, by a process called horizontal gene transfer Artificial Competence Involves lab procedures that make the cell passively permeable to DNA METHODS Solution of divalent cations (calcium chloride) under cold conditions, before the application of heat shock Electroporation, involves application of 10-20kv/cm, which creates holes in cell through which plasmid DNA enters Basic Principle Of Transformation Genes can be cut out of human, animal or plant DNA placed inside bacteria and the bacteria will produce the “foreign” protein coded for by the gene. For example, a healthy human gene for the hormone insulin can be put into bacteria. Under the right conditions, these bacteria can make authentic human insulin just as they would make their own proteins. What is a plasmid? A plasmid is a small circle of DNA. Ampicillin is an antibiotic; antibiotics prevent bacteria from growing. Cell membrane Bacterial chromosomal DNA *plasmids* Transformation Procedure TEST TIME!!! Place the Stages of Transformation in Order: C,B,D,E,A Results THANK YOU