* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Karotype Chromosomal Abnormalities
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
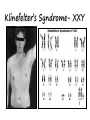
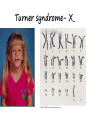
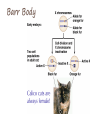
DO NOW Are genetic differences good? In your groups, brainstorm 3 reasons why genetic diversity can be beneficial KARYOTYPE & CHROMOSOME IRREGULARITIES Karyotype A picture of chromosomes used to detect chromosomal abnormalities. Autosomal (somatic): Pairs 1-22 Sex: Pair 23 Non-disjunction Mutations CAUSE: Chromosomes don’t separate correctly during anaphase EFFECT: gametes with irregular chromosome number replication error of error of crossing over Changes in chromosome structure Deletion loss of a chromosomal segment Duplication repeat a segment Inversion reverses a segment Translocation move segment from one chromosome to another Single Chromosome Mutations Autosomal Chromosomes: 1. Down Syndrome- Trisomy #21 Sex Chromosomes: 1. Turner’s Syndrome (X)- Monosomy X 2. 3. 4. Female, sterile, heart defects Male, but have some female characteristics (Extra breast tissue) Kleinfelter’s Syndrome (XXY) Jacob’s Syndrome (XYY) Not huge effect, problems in testes fertility Not a problem, every x chromosome except 1 is turned into an inactive, Barr Body XXX 1. Ex. Calico Cats always female Klinefelter’s Syndrome- XXY Turner syndrome- X_ Down Syndrome & Age of mother Mother’s age Incidence of Down Syndrome Under 30 <1 in 1000 30 1 in 900 35 1 in 400 36 1 in 300 37 1 in 230 38 1 in 180 39 1 in 135 40 1 in 105 42 1 in 60 44 1 in 35 46 1 in 20 48 1 in 16 49 1 in 12 Barr Body Chromosome Set Mutations Extra Sets = “ PLOIDY” Common in plants/fungi, usually not successful in animals Can lead to evolution! PROKARYOTIC GENETIC EXCHANGE Prokaryotic Genetics Haploid Reproduce by Binary Fission Reproduce, and MUTATE very easily Bacterial Conjugation: “Sex Pilus” connects 2 cells & passes genetic material Genetics recombine Plasmid Prokaryotes have 1 circular chromosomes AND small DNA molecules called PLASMIDS Plasmids move easily during Conjugation HUMANS ARE COOL, BUT WHY IS IT BETTER TO BE A BACTERIA? Genetic changes increase survival and can lead to evolution!