* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic disorders
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
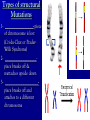
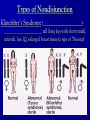
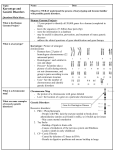
Genetic disorders Caused by: ~ _________________________ ________________________ Or ~ _________________________ _________________________ Altered Chromosomes # can change due to _________________ __________________________________ structure can change _______________ __________________________________ __________________________________ ( Remember: chromosomes are DNA wrapped around histones. When the DNA is altered the structure changes) ________ - & _________ Substance that can cause 1- _______________ Mutationreproductive cells (sperm & a mutation egg) - Ex- UV Light 2- __________ Mutation- body - X-Rays cells (types of Cancer) - Radiation - Viruses - Tobacco Types of structural Mutations 1- ________________- piece of chromosome is lost (Cri-du-Chat or PraderWilli Syndrome) 2- __________________piece breaks off & reattaches upside down 3- ___________________piece breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome 4- ____________________- removal of a single DNA nucleotide (one nitrogen base is substituted with another) Example** Original - The fat cat ate the wee rat. ** Point Mutation - The fat hat ate the wee rat. Carcinogen- mutation that may cause cancer Cri du Chat Syndrome: ___________ Characteristics - High pitched mewing cry as an infant - Slant of the eyes - Mental retardation - _________________ __________________ __________________ Prader –Willi Syndrome: _____________ Characteristics - Infants are weak- sucking reflex is poor & feeding is difficult - _______________________ ______________________ - Children become extremely obese - ______________________ - Short stature - Poor sexual development - Behavioral issues Changes in the Chromosome Number _______________________- chromosomes fail to separate during Meiosis; will cause a lack of a chromosomes or will give you an extra chromosome 2 Types 1- _______________- lack a chromosome _________________________________ - _______ chromosomes = XO -________________________ - webbed neck - short - swelling at wrists & ankles - ______________________________ - 2. Trisomy- ___________________________ - ex: __________________(Trisomy 21)- males & females, decreased muscle tone, slanting eyes, small mouth with protruding tongue, mental retardation Types of Nondisjunction Klinefelter’s Syndrome (______________________)_____________________, tall (long legs with short trunk), infertile, low IQ, enlarged breast tissue (a type of Trisomy) Detecting Human Genetic Disorders Genetic screening- examine a person’s genetic make-up (Karyotype, Blood tests) 2 methods: 1- ____________________amniotic fluid withdrawal 2- ____________________ (CVS)- take a sample of villi (_____________________ _____________________) **Both produce Karyotype** Detecting Human Genetic Disorders Advantage of both: - Physicians can detect more than _________________________________ Disadvantage of Amniocentesis: most conditions are incurable and the results ____________________________________ (abortion at this time is very difficult) Disadvantage of CVS: __________________ ________________________or miscarriage but it comes back b/4 1st trimester is over Genetic Traits & Disorders Genetic Disorder- disease or set of conditions that have a genetic basis. 1- Single Allele Trait- 1 allele controls the trait A) ____________________: Ex: Huntington’s disease, Achondroplasia (dwarfism), Cataracts, Polydactyl) B) _____________________: Ex: albinism, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, PKU, Marfan Genetic Traits & Disorders 2.- ______________________ 3 or more alleles of the same gene code for a single trait Ex- Blood Groups (A, B, O) 3- ______________________traits that are controlled by many genes (Skin, Hair & Eye color, Height, Foot size) 4- ______________________phenotype depends on gender and hormones (Baldness) Genetic Traits & Disorders 5- __________________found only one the X Chromosome ExamplesColorblindness, Fragile- X, Hemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy, Ichthyosis simplex (Scaly skin) Heterozygous advantage Malaria and sickle cell anemia _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________