* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Connection (pgs.101-106)
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
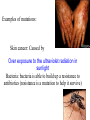
Introduction to Genetic Disorders Project Background Information The function of genes To control the production of proteins in the organism's cells. Proteins help Determine the size, shape, and many other traits of organisms The 4 different bases of DNA Adenine - (A) Thymine - (T) Guanine - (G) Cytosine - (C) A single gene can contain Several hundred to a million or more bases The order of the nitrogen bases Along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. A mutation is NOT A mutation is NOT A mutation is Any change in a gene or chromosome Causes for a mutation The Substitution of a single base for another When chromosomes don't separate correctly during meiosis If a mutation happens in a body cell, it will only affect The cells that carries it (only that person) If a mutation happens in a sex cell, it can be Passed on to an offspring and affect the offspring phenotype Some mutations are harmful, some are helpful some are neither Helpful nor ___________ harmful ____________ Examples of mutations: Skin cancer: Caused by Over exposure to the ultraviolet radiation in sunlight Bacteria: bacteria is able to build up a resistance to antibiotics (resistance is a mutation to help it survive) Human Inheritance Chromosomes ______________ determines if a person is male or female. What are the two chromosomes for a female? What are the two chromosomes for a male? X the egg in a female only carries the ____ chromosome. X or _____ Y The sperm in the male can carry the ______ chromosome. Looking at the Punnet Square, what is the probability that the couple will have a boy? A girl? 50/50 X Y X XX XY X XX XY Human Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is Abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes Genetic disorders are caused by Mutations or changes in a person's DNA Achondroplasia Wilson Disease Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD) Cystic Fibrosis Charcot-Marie-Tooth Down Syndrome Duane Syndrome Familial Hypercholesterolemia Gaucher Disease Fragile X Syndrome Hemochromatosis Hemophilia Huntington’s Disease Klinefelter Syndrome Marfan Syndrome Noonan Syndrome Osteogenisis Imperfecta Phenylketonuria Progeria Porphyria Sickle-Cell Turner Syndrome WAGR Syndrome What Questions do you Expect to Answer Through Research? Types of Websites to Avoid Sites that are too difficult to understand Wikipedia – although much of the information is now considered to be accurate, it is a site that can be edited by anyone. To begin: go to www.genome.gov/10001204