* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Karyotypes and Mutations
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
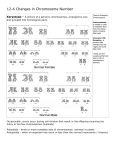
• When does crossing over occur? When does independent assortment occur? • Describe the cells that result at the end of meiosis • TAKE OUT YOUR MEIOSIS vs MITOSIS AND MITOSIS FOLD TO BE STAMPED Chapter 12 Section 1 • All of an organism’s DNA can be packaged into chromosomes • Humans - 23 pairs or 46 total chromosomes • Chromosome Numbers • 1-22 autosomes • Sex chromosomes “#23” • XX – Female • XY - Male • A karyotype is a picture of all chromosomes in a cell, for one organism • Karyotypes can show: • changes in chromosomes • deletion of part or loss of a chromosome • extra chromosomes Male Female • A change in a genetic trait •1) chromosomal •2) gene mutation • Germ cell (gametes) or somatic cell (body) •Germ cell mutations can be inherited and somatic cell mutations result in cancers • Can be lethal (even before birth) •loss of a piece of chromosome •Cri du chat (#5) •Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (#4) • Inversion: chromosome breaks off and reattaches in reverse • Translocation: piece breaks off and attaches to another • * No problems in an individual since all genes are intact but there are problems with crossing over during meiosis • Nondisjunction: failure of a chromosome to separate from its homologous chromosome • Trisomy - one too many chromosomes (2n=47) • EX Down Syndrome, Kleinfelter’s Syndrome (XXY) • Monosomy - only one of a homologous pair (2n=45) • EX. Turner Syndrome (X)