* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Inheritance - Mr. Lincoln`s Science Wikipage!
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
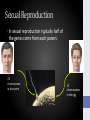
Genetic Inheritance Objective • Describe sexual and asexual mechanisms for passing genetic materials from generation to generation. Genes • Hereditary information is contained in genes. • Genes are composed of DNA that makes up the chromosomes of cells. Genes • Each gene carries a single unit of information. • A human cell contains thousands of different genes. Gene Each Cell = Full set of genes • Each human cell contains a copy of all the genes needed to produce a human being. Genetic Inheritance Unattached earlobes (Dominant) Attached earlobes (Recessive) • A single inherited trait of an individual can be determined by one pair or by many pairs of genes. Genetic Inheritance • A single inherited trait of an individual can be determined by one pair or by many pairs of genes. Asexual Reproduction • In asexual reproduction, all the genes come from a single parent. • Asexually produced offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Asexual Reproduction • In asexual reproduction, all the genes come from a single parent. • Asexually produced offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual Reproduction • In sexual reproduction typically half of the genes come from each parent. 23 chromosomes in the sperm 23 chromosomes in the egg Sexual Reproduction • In sexual reproduction typically half of the genes come from each parent. 46 chromosomes in the zygote Sexual Reproduction • Sexually produced offspring are not identical to either parent. The Lincoln Family Objectives • Describe simple mechanisms related to the inheritance of some physical traits in offspring. Genetic Inheritance • In all organisms, genetic traits are passed on from generation to generation. Dominant vs. Recessive traits • Some genes are dominant and some Dominant are recessive. Dominant Dominant Recessive Recessive Recessive Genetic Probability The probability of traits being expressed can be determined using models of genetic inheritance. Punnet Squares • Some models of prediction are pedigree charts and Punnett squares. R= round r= wrinkled Green vs. Yellow Pea Pods G= g= Pedigree Chart Pedigree Chart Incomplete Dominance • Some traits are inherited by mechanisms other than dominance and recessiveness.