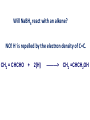* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reactions of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
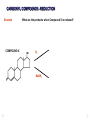
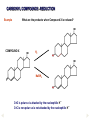
REACTIONS OF AlDEHYDES AND KETONES L.O.: Outline the mechanism for nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones with hydrides. Nucleophile: is a atom or groups of atoms attracted to an electron-deficient centre, where it donates a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond A curly arrow is a symbol used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of an electron pair in the braking or forming of a covalent bond Mechanism: Reduction of an aldehyde by nucleophilic addition The reduction of an aldehyde You get exactly the same organic product whether you use lithium tetrahydridoaluminate or sodium tetrahydridoborate. For example, with ethanal you get ethanol: Reduction of an aldehyde leads to a primary alcohol. Reaction summary: Reduction: Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a reducing agent. It provides a source of hydrogen and also allows hydrogen to act as a nucleophile by creating H-. It can be represented by [H]. Many reducing agents will reduce ketones and aldehydes to alcohols. NaBH4 (sodium tetrahydroborate(III) ) generates the nucleophile H-, the hydride ion. Write the mechanism of the reaction of a ketone/aldehyde with H-. Will NaBH4 react with an alkene? NO! H- is repelled by the electron density of C=C. CH2 = CHCHO + 2[H] ———> CH2 =CHCH2OH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - REDUCTION Example COMPOUND X What are the products when Compound X is reduced? H2 NaBH4 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - REDUCTION Example What are the products when Compound X is reduced? COMPOUND X H2 NaBH4 C=O is polar so is attacked by the nucleophilic H¯ C=C is non-polar so is not attacked by the nucleophilic H¯ Page 43, Q5