* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology: Cell Unit Review
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
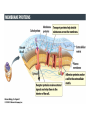
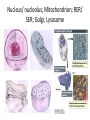
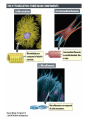
Biology: Cell Review Modern Biology©2009 Holt, Rinehart, & Winston Chapter 4 Cell History • Robert Hooke, 1665, saw cork under light microscope, and called individual units “cells”. • van Leeuwenhoek, 1673, saw living cells under microscope with 10x greater magnification • M. Schleiden, 1838, said all plants were made of cells • T. Schwann, 1839, said all animals were too. • R. Virchow (1821-1902) said all cells came from preexisting cells First Cells Seen Hooke’s Cork Cells Leeuwenhoek’s Giardia cells Cell Theory • Has 3 essential parts: Cells come only from reproduction of existing cells. Cells are basic unit of structure & function in organisms. All living organisms are composed of 1 or more cells. Cell Structure • Form follows function: Shapes evolve to allow cells to perform their function. • Sizes range from nm to 2 m in length, but average cells are 10 – 50 mm. • Surface-area-to-volume ratio limits size. – Volume increases more quickly. – Cells’ need for nutrient intake & waste disposal depends on proximity to cell membrane. Cell Types Two basic types 1. Prokaryotic i. Has no membrane-bound organelles or nucleus ii. Is divided into 2 domains a) b) Bacteria – similar to 1st cellular life forms Archaea 2. Eukaryotic i. Has membrane-bound organelles, including nucleus Protists (from earlier lab) Plasma Membrane • Phospholipid bilayer – Outer & inner phosphate heads are polar – Inner portion composed of lipid tails • • • • Regulates passage in/ out of cell Separates cellular activities from environment Interfaces with environment Includes integral & peripheral proteins & lipids (sterols) Fluid Mosaic Model Cellular Organelles & Functions • • • • • Nucleus: houses/protects genetic info (DNA) Nucleolus: site of ribosomal RNA production Mitochondrion: energy production Ribosomes: protein production Endoplasmic reticulum: intracellular highway – RER: phospholipids & proteins; SER: lipids + detox • Golgi apparatus: sort/package proteins + lipids • Lysosomes: digest large molecules & invaders • Peroxisomes: break down R-OH, f.a., bacteria Nucleus/ nucleolus; Mitochondrion; RER/ SER; Golgi; Lysosome Cytoskeleton • • • • Network crisscrossing cytoplasm Gives shape to cell Acts as system of internal tracks Has 3 structural elements – Microtubules: made of tubulin; make flagella/cilia • Centrioles: organize microtubules in cell division – Microfilaments: made of actin, help in cell movement – Intermediate filaments: rods: anchor nucleus et al, make up hair shaft Plant Cells • Unique Structures but have no centrioles – Cell Wall: primary + secondary • Made of cellulose – Central Vacuole • Made as smaller vacuoles fuse together • Stores water, enzymes, wastes, etc… – Plastids • Chloroplast: site of photosynthesis • Chromoplast: has colored pigments + photosynthesis • Amyloplasts: store starch