* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Projections of Future Climate Change
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
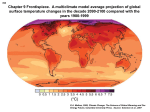
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
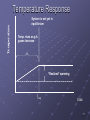
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
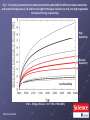
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
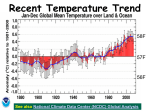
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
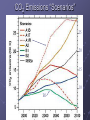
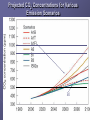
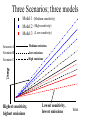
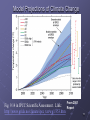
Lecture 15: Projections of Future Climate Change Global Mean Temperature 1 21st Century Climate Change Dominant influence likely to be increase in greenhouse gases (anthropogenic) Projections of temperature change are made using climate models 2 Climate Models – 1 (Not Necessary) A climate model is a mathematical representation of the physical processes that control climate Equations are complicated: Computers are used to solve them 3 Climate Models –2 (Not Necessary) The most sophisticated climate models are called General Circulation Models (GCMs) These models attempt to simulate all processes in the atmosphere and ocean relevant to climate 4 Climate Models – 3 Input Anthropogenic forcing Climate Model Output Climate change 5 Emission Scenarios Emission scenario: Possible future emissions Reference: http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/029. htm 6 CO2 Emissions “Scenarios” 25 20 15 10 B1 7 Calculation of Future CO2 Concentrations -- Method Model Input Anthropogenic Emissions Carbon Cycle Model Model output CO2 Concentration increase 8 Projected CO2 Concentrations for Various Emission Scenarios B1 B1 9 Some Scenario Results Scenario Characterization A1FI B1 B2 Rapid economic growth; strong reliance on fossil fuels Moderate economic growth; much less reliance on fossil fuels “Middle-of-the-road” scenario Emission CO2 Rate in Concentration 2100 in 2100 (ppm) (Pg/yr) 28 980 5 550 13 700 10 Past and Projected Future CO2 Concentrations on same graph See the IPCC Synthesis Report, Summary for Policymakers, Figure SPM-10a, p. 33. (URL: http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/vol4/engli sh/fig9-1a.htm) 11 Climate Models -- 5 Complication: Models have differing sensitivities models produce different results for same emission scenarios 12 Differing Response of Models for Same Scenario Time 13 Three Scenarios; three models Model 1 (Medium sensitivity) Model 2 (High sensitivity) Model 3 (Low sensitivity) Scenario A Scenario B Scenario C Highest sensitivity, highest emissions Medium emissions Low emissions High emissions Lowest sensitivity, lowest emissions time 14 Model Projections of Climate Change Fig. 9.14 in IPCC Scientific Assessment. Link: http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/353.htm From 2001 Report 15 Summary: Two Causes for Large Range in Projections 1. Wide range in emission scenarios 2. Wide range in model sensitivities #1 due to uncertainty in future human actions (i.e., it is not a fault of the models) #2 is due to our imperfect understanding of the climate system (i.e., it is a fault of the models) 16 From 2007 Report 17 Model Projections Average temp. for 2090-2100 compared to average for 1980 – 1990. All models project warming for all scenarios Range: 1.1C – 6.4C 18 Meaning Low end: warming of 1.1C Achievable IF 1. 2. Emissions are cut significantly Lowest-sensitivity model is correct High end: Warming of 6.4 C May occur if 1. 2. Emissions continue to rapidly increase Highest-sensitivity model is correct 19 Constant Concentrations Suppose concentrations of greenhouse gases have been rising, but suddenly stopped rising at time = tstop tstop time 20 Temperature Temperature Response System is not yet in equilibrium Temp. rises as g.h. gases increase “Realized” warming tstop time 21 Realized Warming This is the warming that has been observed at time tstop 22 Temperature Temperature Response Additional Warming “Realized” warming tstop time Warming continues until equilibrium is restored 23 Warming Commitment Def: Warming that will occur in the future due to greenhouse gases added in the past Doesn’t include effect of any future increases in greenhouse gases 24 Fig. 1. CC warming commitment (constant concentrations after 2000) for different climate sensitivities and aerosol forcing levels (L, M, and H on the right of the figure indicate low, mid-, and high magnitudes for aerosol forcing, respectively) High Sensitivity Medium Sensitivity Low Sensitivity T. M. L. Wigley Science 307, 1766 -1769 (2005) Published by AAAS 25 Meaning of Graphs With greenhouse-gas composition constant at 2000 levels, Earth would warm for centuries (warming commitment) Commitment depends on sensitivity and amount of aerosol forcing Mid-range estimate: Commitment ~ 0.5C High-end estimate: Commitment ~ 1C This is warming that is “in the pipeline” 26 Reducing Commitment Only way: Reduce amount of greenhouse gas in atmosphere The sooner the reductions occur, the greater the reduction in the commitment Problem: Removing greenhouse gases is very difficult! More later 27 Principal Difficulty CO2 mixing ratio is 380 ppm i.e., only 380 out of every million molecules of air are CO2 CO2 removal would require processing enormous amounts of air Lots of energy probably required. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/6 345557.stm 28 What the link reveals Branson launches $25m climate bid 29 Another Problem Removing CO2 would create waste Where should it be stored? 30 Carbon Capture and Storage Would reduce future emissions, but wouldn’t actually remove CO2 from atmosphere http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/6 345557.stm#carbon 31 Carbon Sequestration 32