* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
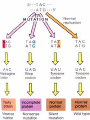
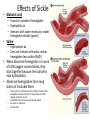
Ch. 16 Part 3: Mutations Mutations • Unpredictable change in the genetic material – Gene Mutation: change in structure of a DNA molecule that produces a different allele of a gene – Chromosomal mutation (ABERRATION): changes in the structure or number of chromosomes in an organism • Give rise to new alleles • Causes: – Random – Environmental factors (increase chances) • Ionizing radiation • UV Radiation • Chemicals MUTAGEN! Gene Mutations • 3 Main types – Point Mutation • Base Substitutions – May lead to silent mutation (mutation with no apparent affect on organism) – Frameshift Mutation (significant effect) • Base addition (insertion) • Base deletion (deletion) Base Substitution Replacement of one base or nucleotide with another Usually do not change amino acid Sometimes causes a change in the protein made Silent Mutation When a substitution does not cause a change in the protein expressed by a gene Remember some codons represent the same amino acid Example: GAA and GAG both code for Glu • Point Mutation A point mutation is a simple change in one base of the gene sequence. This is equivalent to changing one letter in a sentence, such as this example, where we change the 'c' in cat to an 'h': Original: The fat cat ate the wee rat. Point Mutation: The fat hat ate the wee rat. Insertion or Deletion Nucleotide is removed or added More disastrous mRNA is read as triplet codes Adding/removing bases changes these three letter codes Codons downstream from insertion/deletion will be regrouped and probably code for a non-working protein Result: FRAMESHIFT MUTATION Shift the “reading” frame of the genetic message • • Frameshift mutation The fat cat ate the wee rat. Original: Frame Shift: The fat caa tet hew eer at. Sickle Cell Anemia • • • • Sickle cell anemia 1/500 African Americans have the disorder Co-dominant allele Causes blockages in blood vessels, preventing oxygen from getting to other cells and tissues • Beneficial in central and east Africa because it helped destroy malaria – If you had SCA, your body would destroy the sickle cells to protect itself and in the process, destroy the malaria parasite as well DNA and Sickle Cell Anemia • Review hemoglobin – 2 alpha chains – 2 beta chain HbA allele: allele for normal B-globin polypeptide HbS allele: allele for normal B-globin polypeptide • Sickle Cell Anemia – Inherited blood disorder HbAHbA : Normal HbAHbS : Normal but carrier HbSHbS: sickle cell anemia • BASE SUBSTITUTION Mutation to DNA sequence that codes for beta chains – One DNA nucleotide is replaced with a different nucleotide • Normal amino acid sequence for beta chain: – VAL-HIS-LEU-THR-PRO-GLU-GLU-LYS– HbA allele (normal hemoglobin allele) – DNA triplet code for Glu is CTT • Mutated amino acid sequence for beta chain: – VAL-HIS-LEU-THR-PRO-VAL-GLU-LYS– HbS allele (sickle cell allele) – DNA triplet code for CTT is changed to CAT, which no longer codes for Glu, but instead Valine Effects of Sickle Cell Mutation • Glutamic acid – Found on outside of hemoglobin – Hydrophilic aa – Interacts with water molecules, makes hemoglobin soluble (good!) • Valine – Hydrophobic aa – Does not interact with water, makes hemoglobin less soluble (BAD!) • When abnormal hemoglobin is in area of LOW oxygen concentration, they stick together because the outside is now hydrophobic • Abnormal hemoglobins form long chains of insoluble fibers – – – – These pull the red blood cells that contain the abnormal hemoglobin inwards and out of shape (become sickle shaped instead of round) Sickled RBC cannot move easily through blood Get stuck in capillaries Possibly fatal Albinism • Show relationship between gene, enzyme, and phenotype • Albinism melanin (dark pigment) totally or partially missing from eyes, skin, and hair – Causes: • • • • • • • Pale blue/pink irises Pale skin Pale hair Red pupils Poor vision Jerky movements Inability to absorb light (protection) • Genetic Cause: – Mutation at several LOCI – AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE disorder • Must get TWO recessive alleles to have disorder • 1 in 17000 births – SEX-LINKED version of disorder • Affects only eyes, not skin • TYROSINASE an oxidase enzyme – – – – – 2 copper atoms in active site that bind to oxygen Transmembrane protein In membranes of large organelles in melanocytes called melanosomes Most of protein, including active site in in melanosome Also found in plants • • • • • Enzyme reacts with air (causes blackening of potato) Enzyme TYROSINASE converts amino acid tyrosine into DOPA DOPA is the converted to dopaquinone which is then converted into Melanin Melanin: – dark brown to black pigment occurring in the hair, skin, and iris of the eye – responsible for tanning of skin exposed to sunlight In Albinism: – Mutation of gene results in inactive or absent TYROSINASE – Without TYROSINASE, first two steps of conversion process cannot occur • • • No DOPA No dopaquinone No melanin Huntington’s Disease (HD) • Autosomal Dominant Disorder – Most people with disorder are heterozygous – 1 in 2 chance of passing it off to children • Neurological disorder • Causes involuntary movements (chorea) and mental deterioration • Age on onset is variable Huntington’s Disease (HD) • Caused by mutation – Unstable segment in a gene on chromosome 4 that codes for protein HUNTINGTIN • Protein regularly interacts with proteins found only in the brain • Altered huntingtin is most disruptive to nerve cells, even though it is found throughout the body – Normal gene made of small number of repeats of the triplet of bases CAG – Mutated gene contain larger number of repeats of CAG triplet • STUTTER repeats of triplet • More stutters = earlier age in which condition appears