* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab5CysticFibroShort
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
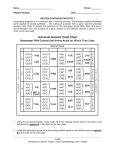
What genetic mutation causes Cystic Fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a recessive, genetic disorder that affects mainly Caucasians. CF affects about one in every 2,500 newborns in the USA. The symptoms of CF include serious digestive and respiratory problems and extremely salty sweat. These symptoms result from the inability of the exocrine glands to absorb chlorine and sodium. As a result, thick, sticky secretions clog up the tubules in the linings of internal organs irreversibly damaging them. The damage is so severe CF patients die an early death. 60 years ago most CF patients died as babies. Now most in the United States live into their late 30s. The Cystic Fibrosis Gene To find the CF gene, geneticists looked for markers (fragments of identifiable DNA) on specific chromosomes by comparing the DNA of CF-affected individuals to DNA of people without the disease. Eventually, it was determined that the gene codes for a protein channel and is located on chromosome 7. You will read 24 bases of the 250,000 that code for the CFTR protein channel. From these bases you will be able to determine 8 amino acids that form a key part of the protein channel. Figure 1.3 represents the bases present in a small part of the gene for CF (from one chromosome) for six different high school students. The entire CF gene contains about 250,000 bases-far too many to list on this page. Figure 1.1 1. Read the 10 bases in the boxed part of Figure 1.2. In your journal list the 10 from top to bottom. 2. Copy the table header and put 8 rows below it. (5 columns, 10 rows) Amino Acid Sequences Amino Acid # Norma Josina Leah (CF) 1. Richard (CF) 3. Read the bases for Norma, Josina, Leah and Richard in Figure 1.3 and use the table in Figure 1.4 to determine the Amino Acid names. Name the correct amino acids in your table. 4. One critical part of the protein is coded for by bases 13, 14 & 15. Look at Fig 1.3 again and list the bases 13, 14 & 15 for all 4 people. 5. Every person has a different sequence of bases for 13, 14 & 15 yet only Leah and Richard Have CF. Why doesn’t Josina’s difference cause CF? 6. Use a colored pencil to circle the amino acid differences between the 4 people in your table. 7. Compare Leah’s amino acid sequence to that of Norma and Josina. Use the handout of amino acid structure (“Standard Genetic Code”) to explain what is different about Leah’s amino acid that causes CF. 8. Compare Richard’s amino acid sequence to that of Norma and Josina. Use the handout of amino acid structure (“Standard Genetic Code”) to explain what is different about Richard’s amino acid that causes CF. Copy the questions and answer. 1. Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder. That means that affected individuals have inherited an abnormal allele from each parent. Would a person who has a sequence like Leah's and a second sequence like Norma's have CF? 2. Assume that a person has one allele with the sequence shown for Leah and a second allele with the sequence shown for Richard. Would the person have CF? Explain your answer. 3. A person can have the same sequence of DNA for the 24 bases as does Josina and still have CF. Propose a hypothesis to explain this. How might you test your hypothesis if you had the ability to read the complete CF gene? Remember that the 24 bases of the DNA sequence you have examined represent only a small fraction of the DNA (approximately 250,000 bases) found in the CF gene. 4. Consider the steps of protein synthesis and protein folding and explain one or more probable causes of mutations that result in diseases like Cystic Fibrosis.