* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
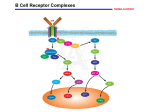
Antigen-independent development of B cells B cell subsets and development Fetus liver:B1 B Bone Marrow: HSC proB mB spleen:NF B FO B FP MZ B preB imB three major naive peripheral B-cell populations B cell High-affinity IgG Immunol Rev 2004; 197:206 INSTITUTE FOR IMMUNOBIOLOGY B cell and B cell-mediated humoral immune response Part II Department of Immunology Fudan University Wei Xu, Ph.D 021-54237749 [email protected] Overview of the humoral immune response against bacterial B cells plasma cells Significance of humoral immunity eliminate extracellular bacterium and toxin eliminate extracellular virus B cells and humoral immune response 1. Recognition of the specific Ag 2. Activation, proliferation, differentiation 2. Germinal center: later event 3. General feature of Ab response thymus-dependent (TD) antigens B response to TD Ag requires direct contact with Th cells, thymus-independent (TI) antigens TI- 1 Ag bacterial cell-wall components, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), TI-2 Ag highly repetitious molecules, bacterial flagellin bacterial cell-wall polysaccharides with repeating units. Recognition of TD Ag Directly recognize Ag (B cell epitope) No MHC involvement surfaced displayed B cell-epitopes Ab (BCR) binds the B-cell epitope directly, TCR binds with a self-MHC-T-cell-epitope complex BCR-Iga/Igb -coreceptor complex B cell epitope (CD21-CD19-CD81) coreceptor B cell epitope Ag-C3d BCR CR2 Iga/b CD19 Signal Signal + + B cell activation +++ B cells and humoral immune response 1. Recognition of the specific Ag 2. Activation, proliferation, differentiation 2. Germinal center: later event 3. General feature of Ab response 1) activation A. 2-signal activation model B. the help from Th cell 2) Signal transduction 3) Proliferation and differentiation the 2-signal rule signal 1:BCR - B cell epitope signal 2:CD40 - CD40 L B B7 survive Th CD40L survive Co-sti mol B cell activation requires 2 signals Signal 3: IL-4 Signal 1 From antigen Recognition of B cell epitope Receptor-mediated Ag endocytosis T cell epitope-MHC II presentation BCR serves 2 roles: 1. Ag-induced clustering of BCRs delivers signals that initiate the activation process. 2. BCR internalize the Ag into endosome, process and present on surface for T recognition Signal 1 From antigen Signal 3 From Th Signal 2 From Th Antigen crosslinks mIg(BCR), generating signal 1, which leads to increased expression of class II MHC and costimulatory B7. Antigen–BCR complexes are internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis and degraded to peptides, which are bound by class II MHC and presented as peptide–MHC complexes. Th cell recognizes Ag–class II MHC and B7-CD28 co-stimulation on Bcell membrane which activates TH cell. Th cell begins to express CD40L. Interaction of CD40 and CD40L provides signal 2. Th cell release large quantities of cytokines(IL-4) signal 3 to support the progression of the B cell replication and differentiation. Signal 3 Th-secreting cytokines Regulate B cell differentiation B cells and humoral immune response 1. Recognition of the specific Ag 2. Activation, proliferation, differentiation 1) 2-signal activation 2) signal transduction 2. Germinal center: later event 3. General feature of Ab response Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation cascade PTK Src family immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) Bruton’s disease a genetically determined immunodeficiency disease inability to synthesize all classes of antibody. discovered in 1952 by O. C. Bruton. Case: a young boy who had mumps 3 times and experienced 19 different episodes of serious bacterial infections during 4 years. Do not raise Abs to any vaccines. 1937,Tiselius use Electrophoresis to analyze the serum proteins Which comprised of 5 components: albumin、a1、a2、b、g globulin anode Antibody,IgG albumin a globulin b globulin g globulin cathode Electrophoresis Serum of unimmunized person Pathogenesis: failures in B-cell development. inhibition pro–B to pre–B-cell transition In 1990s, the gene was cloned which encodes Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk). Btk play important roles in B-cell signaling vital to the function of mature B cells Absence of Btk results in the failure of B activation and Ab generation B cells and humoral immune response 1. Recognition of the specific Ag 2. Activation, proliferation, differentiation 1) 2-signal activation 2) signal transduction 3) proliferation 2. Germinal center: later event 3. General feature of Ab response Early and late event in Ab response to TD antigen Early events: follicle(B)-paracortex(T)border, B activation and T-B activation Small amounts of Ab production Late events: At the germinal center Presence of Ag and Th Affinity maturation Ig class switch (IgM Memory B IgG) (T cell) Affinity maturation late event in Ab response to TD antigen in LN Ag Th 1、somatic hypermutation 2、affinity maturation 3、Ig class switch Un-activated lymphocyte (mantle zone) Light zone Dark zone Follicular DC (FDC) No MHC II Bind with Ag-Ab (IC )by FcR,maintain Ag for long Provide persistent Ag signal for B cells 1、somatic hypermutation In presence of Ag , by Th’s co-stimulation Point Mutation of CDR in the Ig V region Affinity-enhanced BCR(B cell) is selected affinity maturation 2、affinity maturation Result of somatic hypermutation of B cell B cells with high affinity would survive Affinity enhancement 3、Ig class (isotype) switch In response to CD40-CD40L signal and IL-4 from Th cell, the activated B cells undergo the process of heavy chain isotype (class) switching leading to production of Abs with different class of heavy chain. cytokine determined occur in single B cell during RNA transcription ligation of various C gene the V region of Ig remains, the C region changed Without Th With Th’ help Th cell-secreting cytokines determines the Ig class switch No Th CD40L signal、IL-4 from Th The V gene would recombine with a downstream C region gene and the other DNA deleted IgM IgG late event in Ab response to TD antigen in BM Ag Th 1、somatic hypermutation 2、affinity maturation 3、Ig class switch (Th’s help) 5) Fate of the activated B cell plasma cell,PC move to BM? Secret high level of Abs memory B cell maintain in BM? Never die? 1.plasma cell marginal-zone B plasma cells Early stage follicular B later plasma cells short-lived form a germinal centre Th plasma cells follicle Bm long-lived plasma cell Bone Marrow Formation of plasma cells Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5:232 Long-lived plasma cells in the bone marrow somatic mutation class-switch Germinal Center CXCR4 plasma cells crucial survival signals (BM) BAFF- BCMA IL-6- IL-6R B-cellactivating factor survival signals 内皮细胞选择素 血管细胞黏附分子 retention of plasma cells in BM BCMA: receptor B-cell maturation antigen B cell response to TI antigen CD5+B1 Low-affinity IgM No help from Th No class switch (no IgG) Mitogen receptor Signal 1:Ag Signal 2:mitogen Polyclonal strong B activation BCR Mitogen receptor B cell response to TI-2 antigen Repetitive units Signal 1:cross-linking of lots of BCR By polymeric saccharide B cells and humoral immune response 1. Recognition of the specific Ag 2. Activation, proliferation, differentiation 2. Germinal center: later event 3. General feature of Ab response The general feature of humoral immunity primary response Mostly IgM with low affinity,IgG secondary response Mostly IgG with high affinity and high level primary immune response Mostly IgM, later IgG, low level and affinity ① lag phase: long 5-10 days ② log phase ③ plateu phase short ④ decline phase quickly secondary immune response mB act as APC,with high mB7,and high-affinity BCR, small amounts of Ag can stimulate mB ① long Lag phase: short, 1-3 days,quickly to the top ② strong The Ab level is 10 times more than that of the primary response ③ most IgG enhanced affinity 5-10 days 1-3 days 4、受体修正 (receptor revision) 生发中心内 识别自身抗原的 B 细胞 发生 Ig V(D)J 基因的二次重排, 使 BCR 被修正为针对非自身抗原。 清除自身反应性 B 细胞 使针对外来抗原的 BCR 具有更广泛的多样性。 Where do Th and B cell encounter ? follicle(B)-paracortex(T)boundary (T cell) 滤泡区:B Ag特异性 T (蓝色) 向滤泡边缘移动 副皮质区:T B T Ag特异性 B (蓝色) 向滤泡边缘移动 Ag特异性 T (棕色) Ag特异性 B (蓝色) 在滤泡边缘相遇