* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Alive! - Harrison High School
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
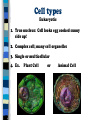
Cells Alive! Cell History 1. The invention of microscope led to the study of cells 2. Notable Scientists a. Robert Hooke: 1st to describe the cell b. Schleiden: Plants are composed of cells c. Schwann: Animals are composed of cells Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function 3. All cells come from preexisting cells (Virchow) Cell Types Two Types: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Prokaryotic 1. No true Nucleus: Nuclear material scattered like a scrambled egg 2. Simple cell; very few cell organelles 3. Most are unicellular 4. Ex. e. coli bacteria Cell types Eukaryotic 1. True nucleus: Cell looks egg cooked sunny side up! 2. Complex cell; many cell organelles 3. Single or multicellular 4. Ex. Plant Cell or Animal Cell Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells Centrioles chromosome Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells Animal Cells No Cell Wall No Chloroplasts Irregular Shape Many small Vacuoles Centrioles Lysosomes Plant Cells Cell Wall Chloroplasts Regular Shape One large vacuole No centrioles No Lysosomes Cell Organization Cells>Tissues>Organs>Systems Cells: The basic unit of life Tissues: A group of cells functioning together to perform an activity Organs: Groups of two or tissues working together Systems: A group of organs working together to carry out major life functions