* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
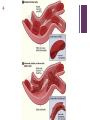
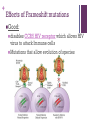
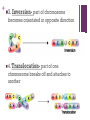
+ Mutations Chapter 12-4 +What are mutations? Any change to the genetic code Causes: Usually error when DNA is being replicated during mitosis environmental factors: UV rays, X-rays, drugs Gene A mutations: change in a single gene + What are mutations? point mutation : Change of 1 or a few nucleotide bases, possibly changing the amino acid coded for Example: Substitutions: one nitrogen base substituted for another + Effects of substitutions Some substitutions result in coding for same amino acid Some change amino acid but doesn’t affect overall protein Some change 1 amino acid and changes structure of entire protein + + Sickle Cell Anemia Normal hemoglobin Sickle Cell Hemoglobin sickle cell video + + Frameshift mutation: Shift in the reading frame that causes every amino acid after the mutation to be different. (Caused by Insertions or deletions) Deletion Insertion + Effects of Frameshift mutations Good: disables CCR5 HIV receptor which allows HIV virus to attack Immune cells Mutations that allow evolution of species + + Negative Examples: Causes disorders: Tay Sachs Chron’s disease Cystic Fibrosis Cancer + Cystic Fibrosis A mutation in the CFTR gene The CFTR gene makes a protein that controls the movement of salt and water in and out of your body's cells. In people who have CF, the gene makes a protein that doesn't work well. 70% of cases caused by this mutation ATCATCTTTGGTGTTTCC lle lle Phe Gly Val Ser ATCAT TGGTGTTTCC lle lle Gly Val Ser + Results of Cystic Fibrosis Thick mucus is produced by the body Mucus fills lungs causing lung infections Mucus blocks pancreas which causes digestive problems Mucus can block bile ducts in liver causing liver failure. + Cancer results from a series of mutations within a single cell Often, a faulty, damaged, or missing p53 gene is to blame The p53 gene makes a protein that stops cells from dividing Without this protein, cells divide unchecked and become tumors. + Tay Sachs The HEXA gene makes part of an enzyme called beta-hexosaminidase A enzyme helps break down a fatty substance called GM2 ganglioside in nerve cells of brain Mutations in the HEXA gene disrupt the activity of beta-hexosaminidase A, preventing the breakdown of the fatty substances. As a result, the fatty substances accumulate to deadly levels in the brain and spinal cord. The buildup of GM2 ganglioside causes progressive damage to the nerve cells +What are mutations? Chromosomal mutations: may change the location of genes and number of genes 4 Types: 1) Deletion: Loss of part/all of chromosome 2) Duplication: Segment is repeated + 3. Inversion- part of chromosome becomes orientated in opposite direction 4. Translocation- part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another + Intro to Cancer Biology video