* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
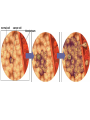
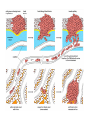
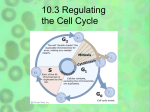
Fun Fact! • There are over 200 different types of cells in the human body, each performing specific functions! – Nerve cells, eye cells, cardiac cells, etc. Do all types of cells go through the cell cycle at the same rate? NO! Some cells divide quickly & some divide slowly. Some types of cells do not undergo cell division at all! Different cell types divide at different rates! • Muscle & nerve cells do not divide once they have developed. – Has anyone ever told you that once you kill your brain cells, you don’t get them back? • Skin cells & cells in the bone marrow divide rapidly. Regulating the Cell Cycle Control of Cell Division • Cell growth & cell division can be turned on & off. When you’re injured, your cells divide rapidly to repair the injury. When the injury has healed, the cells stop dividing. Regulation of the Cell Cycle • Controlling the cell cycle is necessary for healthy growth. • Internal & external factors regulate cell division. – External factors include physical & chemical signals. – Internal factors include proteins that control cell division. For example… • Apoptosis is programmed cell death, or “cell suicide”. – A normal feature of healthy organisms – Caused by a cell’s production of self-destructive enzymes Webbing of the fingers & toes is normal in developing infants. Before the baby is born, apoptosis occurs & enzymes destroy the extra tissues between the fingers. Uncontrolled Cell Growth What happens when your cells lose control & cannot regulate their cell cycle? • When cells in your body cannot control cell growth & division, cancer may form. • Cancer cells cannot respond to the signals that regulate the division of cells. Uncontrolled Cell Growth • When cancer cells have been dividing uncontrollably, tumors form. • Tumors can damage surrounding tissue. • Cells from tumors can break free & travel to other parts of the body, forming new tumors. Uncontrolled Cell Growth Most mammal cells form a single layer in a culture dish & stop dividing once they touch other cells. Cancer cells do not carry out necessary functions. They come from normal cells with damage to genes involved in cell cycle regulation. Carcinogens • Substances known to promote cancer • Some reasons that cells may lose the ability to control growth: – Smoking – Radiation Exposure – Viral Infection • Scientists who study cancer research how cells divide. Treatment • There are several methods of treating cancer. • Standard cancer treatments typically kill both cancerous cells & healthy cells. – This is why there are so many side effects.