* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.3 Notes
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
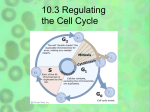
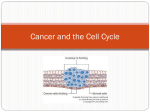
10.3 Notes Regulating Cell Growth 1. Controls on Cell Division a. Cyclins i. In the early ___________ biologists discovered a protein that when injected into cells could cause spindles to form it was called __________. This protein is found in cells that were undergoing mitosis. ii. Called cyclin because it seems to regulate the ___________ cycle. Since its discovery a whole family of cyclins have been discovered that control the timing of the cell cycle in _______________________ cells. b. Regulatory Proteins i. Scientists have since discovered _______________ of other proteins that help to regulate the cell cycle. ii. There are ______________ regulators that allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have occurred inside the cell(ex: chromosome duplication, spindle fibers formed) iii. There are also _____________ regulators respond to events outside of the cell and direct cells to either speed up or slow down the cycle. 1. Ex: Growth factors that stimulate the growth and ___________ of cells. Very important during embryonic development and _____________ healing. 2. Other proteins will ____________ the cell cycle to keep too much growth from occuring. c. Apoptosis i. Cells die in one of two ways: damage/injury or apoptosis. ii. Apoptosis is the __________________ cell death where the cell will go through a series of controlled steps leading to its self-destruction. 1. Cell and chromatin ________________. 2. Parts of the cell ________________ break off. 3. Neighboring cells then quickly clean up the cell’s _______________. iii. A balance of cell growth/death must occur to keep an ________________ healthy. 2. Cancer: Uncontrolled Cell Growth a. How do cancer cells differ from other cells? i. Cancer is a ___________________ in which body cells lose the ability to control growth. ii. Cancer cells do not respond to the ______________ that regulate the growth of most cells. As a result cells will _______________ uncontrollably. iii. Cancer cells form a mass called a _________________. Some are ___________ or noncancerous. However there are others that are _________________ or cancerous. These will spread to invade and destroy surrounding ______________ tissue. These will absorb ________________ needed for other cells. b. What causes cancer? i. Defects in the _______________ that regulate cell growth and division. ii. Examples of sources of defects: smoking or chewing tobacco, radiation exposure, other defective genes, and even _____________ infections. iii. If a cancer cell can spread into the ______________ ______________ then it can effectively move into other parts of the body… this is very bad. c. Treatments for cancer i. Surgery 1. If a tumor is _________________ , and spotted early enough, it can be treated this way. Ex: skin cancer. ii. Radiation 1. If a tumor is growing too fast for surgery then carefully targeted _____________ of radiation can be used to help. iii. Chemical compounds (Chemotherapy) 1. With these compounds one can possible kill cancer cells, or at least __________ their growth. 2. However it also kills non-cancerous cells which causes serious ___________ effects in patients. 3. Much more work is needed to understand the full ____________ cycle in order to see what is truly happening in cell division.