* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Growth - Biology-RHS
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
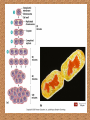
Cellular Growth Chapter 9.1 Main Idea Explain why cells are relatively small in your notes. Cells grow until they reach their size limit, then they either stop growing or divide Cell Size Limitations Most cells are smaller than the period at the end of a sentence. The key factor that limits cell size is the ratio of its surface area to its volume The larger the volume the less efficient the cell As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The larger the surface Area the more efficient the cell This means the cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough waste products. By remaining small, cells have a higher ratio of surface area than volume and can sustain themselves more easily Large animals do not have larger cells, they have more of them. Transport of Substances Recall that the cell membrane controls cellular transport…controls what goes into and out of the cell. Diffusion over large distances is slow and inefficient because it relies on random movement. If the distance to travel becomes too large the cell becomes less efficient Cells remain small to maximize the ability of diffusion and motor proteins to transport nutrients and waste products Cellular communications If the cell becomes to large, it becomes almost impossible for cellular communications, many of which involve movement of substances and signals to various organelles For example: signals that trigger protein synthesis might not reach the ribosome fast enough for protein synthesis to occur The Cell Cycle Once a cell reaches its size limit----it either stops growing or divides Most cells divide—hence how we replace old cells with new ones (RECALL THE CELL THEORY all cells arise from previously existing cells) Cellular reproduction allows you to grow and heal certain injuries Interphase Each time a cell goes through one complete cycle, it becomes two cells G1 Continuous cycles results in continuous production of new cells S G2 Some cells might complete the cycle in as few as 8 minutes Other cells might take up to 1 year Normal cell cycles take approximately 12-24 hours G1 Phase Phase where the cell is growing, carrying out normal cell functions, and preparing to replicate DNA Muscle and nerve cells, exit the cell cycle at this point and do not divide again S Phase Cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division Chromosomes are the structures that contain the genetic material that is passed from generation to generation of cells Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in the cell’s nucleus G2 Phase Phase when the cell prepares for the division of its nucleus. Microtubules for cell division are synthesized at this time The cell also take inventory and makes sure it is ready to continue with mitosis Mitosis and Cytokinesis Phase when cell’s nuclear material divides and separates into opposite ends of the cell Cytokinesis is the actual splitting of the cytoplasm making two daughter cells with identical nuclei Prokaryotic Cell Division Prokaryotes which are bacteria like cells are much simpler cells Prokaryotes reproduce by a process called binary fission