* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bz withdrawal for eapcct 2010
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
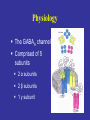
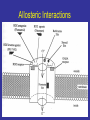
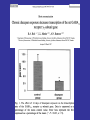
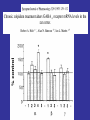
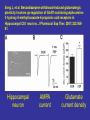
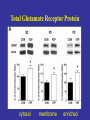
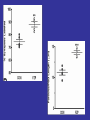
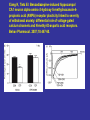
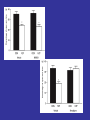
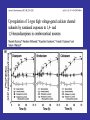
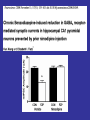
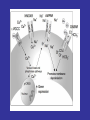
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Robert S. Hoffman, MD Director, NYC Poison Center Objectives History Epidemiology Physiology Treatment History Benzodiazepines are “new” drugs Structure discovered in the 1930s Activity defined in 1957 Chlordiazepoxide marketed in the UK in 1960 Annual USA ER Visits D.A.W.N. Data 2004: 143,546 2005: 189,704 2006: 195,625 2007: 218,640 2008: 271,698 Epidemiology Life time use: 10-15% of men and women Chronic use USA: approximately 2% Denis C, et al: Pharmacological interventions for benzodiazepine mono-dependence management in outpatient settings (Review). Cochrane 2009 1.2 million chronic users in the UK Ashton HC: The Treatment of Benzodiazepine Dependence. Addiction 1994;89:1535-1541 Kan CC, et al Present year dependence rates 40% in general practice patients 63% in psychiatric out-patients 82% in self help patients Dependence 10,861 patients of the Innsbruck University Department of Psychiatry WHO criteria were used for the diagnosis of dependence. Only 9 inpatients and 21 outpatients were addicted to BZs. Fleischhacker: Acta Psychiatrica Scand 2007;74:80 Physiology The GABAA channel Comprised of 5 subunits 2 α subunits 2 β subunits 1 γ subunit Allosteric Interactions Two Central Bz Receptors Both increase Cl conductance Differ in location and effect BZ1 (ω1) Sensory and motor area Sedative, hypnotic BZ2 (ω2) Subcortical and limbic areas Anxiolytic, anticonvulsant BZ Receptor Requirements γ subunit required to recognize benzodiazepines α subunits define the receptor type BZ1 receptor has α1 isoform BZ2 receptors have the α2, α3 or α5 isoforms α4 confers resistance to benzodiazepines GABA Effects of Withdrawal Net Result on GABAA General resistance to benzodiazepines caused by a change in receptor subunit conformation Shift toward BZ2 receptor – tolerance to sedation with some maintenance of anticonvulsant effects Excitatory Amino Acid Effects of Withdrawal Song J, et al. Benzodiazepine withdrawal-induced glutamatergic plasticity involves up-regulation of GluR1-containing alpha-amino3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors in Hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:56981. Hippocampal neuron AMPA current Glutamate current density Total Glutamate Receptor Protein cytosol membrane enriched Xiang K, Tietz EI: Benzodiazepine-induced hippocampal CA1 neuron alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxasole-4propionic acid (AMPA) receptor plasticity linked to severity of withdrawal anxiety: differential role of voltage-gated calcium channels and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. Behav Pharmacol. 2007;18:447-60. Voltage Dependent 2+ Ca Channels Summary Decreased sensitivity of GABAA Change in receptor confirmation Increased sensitivity of Glutamate Change in AMPA receptor number and function Upregulation of L-type (voltage dependent Ca2+ channels Syndrome Poorly described Time course dependent on drug Generally resembles alcohol withdrawal Felt to be relatively mild Diazepam 10 mg q6h x years 10 days earlier diazepam discontinued alprazolam substituted Bizarre behavior, hallucinations agitation BP: 215/125 mm Hg Pulse 130/min Seizures, elevated temperature Given haloperidol Cyanotic cardiac arrest Tex Med 1990;86:44 Alprazolam 1 mg QID for years Abrupt discontinuation 4 days earlier Hypertensive, tachycardic, febrile Lorazepam 2 mg (no response) Continued Haloperidol 20 mg over 24 hours Seizure, hypertension, Oxazepam, metoprolol, alprazolam Seizure cardiac arrest, death Treatment Human No RCT Few uncontrolled trials No large case series Limited animal data Gradual dose reduction +/ Psychotherapy Buspirone, SSRIs, TCAs BB blockers, Carbamazepine, Tiagabine, valproate Aspartate, melatonin Acute Withdrawal Exclude life-threatening illness Fluid and electrolyte managent Benzodiazepine replacement Expect large dose requirements Gentle taper Delirium Above plus Temperature control Barbiturates, propofol, others Avoid neuroleptics Airway management / NMB Consider calcium channel blocker