* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
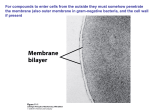
Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for Emerging Therapeutic Applications Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalization strategy that cloaks particles with natural cellular membranes derived from several cellular targets. Refinement of the technique has enabled cell membranes to conform over nanoparticles in a unilamellar and right-side-out manner, effectively functionalizing the particles with membrane lipids and associated membrane proteins. The technique has been applied to cellular membranes derived from red blood cells, platelets, and cancer cells, and the resulting nanoparticles have been shown to adopt numerous cell-like functionalities, including biomimetic interactions with the immune system, toxins, pathogens, and endothelium. Several therapeutic applications, such as long-circulating drug delivery, targeted drug delivery, biodetoxification, and vaccine preparation, were demonstrated with the cell membrane cloaked nanoparticles in animal models. The biomimetic nanoparticles have significant therapeutic potentials in treating cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disease, and infection.