* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry PowerPoint
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
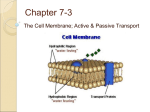
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry By: Mr. Kauffman & Mr. Lowe Outline • Organic Compounds • Cell Parts Review • Biochemical Reactions • Photosynthesis • Cellular Respiration • Fermentation • • • • • • Cellular Transport Diffusion Osmosis Endocytosis Exocytosis 5 Functions Necessary for Life Organic Compounds • All cells are made up of the same basic elements – Carbon (C) – Hydrogen (H) – Nitrogen (N) – Oxygen (O) – Phosphorus (P) – Sulfur (S) • Those elements combine together to form different molecules – Example: Hydrogen + Oxygen = Water Organic Compounds Element Name Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Phosphorus Sulfur Percentage in living things 65.0 % 18.5 % 9.6 % 3.3 % 1.0 % 1.0 % Organic Compounds • 4 Important Molecules for Life Functions 1. Carbohydrates (Carbs) • Function – provides the cell with energy (sugars) • Elements – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen • Example – Glucose, Sucrose, Fructose Organic Compounds • 4 Important Molecules for Life Functions 2. Lipids (Fats) • Function – storage of large amounts of energy for long term use (insulation) • Elements – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus • Example – Fats and Oils Organic Compounds • 4 Important Molecules for Life Functions 3. Proteins • Function – makes up organs and muscles, growth, and repair • Elements – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur • Example – Red meats, Chicken, Fish, Eggs Organic Compounds • 4 Important Molecules for Life Functions 4. Nucleic Acids • Function – instructions for maintenance, growth, and reproduction of cell • Elements – Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus • Example – DNA Cell Parts Review • Nucleus – control center of the cell • Cell membrane – protective outer layer found in all cells • Cell wall – protective outer layer found only in plant cells • Mitochondria – produces energy for cells by breaking down food molecules • Chloroplast – produces energy for plant cells by converting sunlight into sugar Biochemical Reactions • Biochemical Reactions: reactions that occur inside the cells of living things in order to produce energy necessary for life – All cells require energy to carry out the functions necessary for life – The energy that all cells use is in the form of sugars Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis: how plant cells are able to convert sunlight into sugar (energy source) – Happens only in plant cells – Occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells • Contain chlorophyll (green pigment – coloring) Photosynthesis – Sunlight + Water + Carbon Dioxide = Sugar and Oxygen – Plants use some of the energy and store the rest as sugar • Sugar stored in the plant is food for the animals that eat plants – Oxygen produced is released into the air Cellular Respiration • Cellular Respiration: process by which cells convert sugars into chemical energy – Happens in both plant and animal cells – Occurs in the mitochondria of plant and animal cells Cellular Respiration – Sugar + Oxygen = Chemical Energy + Water + Carbon Dioxide – Chemical energy produced is used to complete other cell functions • Growth, repair, cell division, transportation of materials, etc… – Chemical energy not used for cellular functions is released as heat – Carbon dioxide produced is released by the cell and exhaled into the air Fermentation • Fermentation: energy production that occurs in cells without oxygen – An inefficient way to produce energy • Produces only a small amount of energy • Produces lactic acid (the burning you feel in muscles when running/exercising) Cellular Transport • The human body needs to transport materials to the correct cells around the body • Cells need to be able to move these materials into and out of the cell Circulatory System • Circulatory System: organ system responsible for transporting materials to various cells around the body – Consists of the heart, veins, and arteries – Delivers oxygen and nutrients (food) to the cells for energy production – Delivers carbon dioxide to cells in the lungs to be released during exhaling Circulatory System Cellular Transport • Cellular Transport: the movement of materials (water or nutrients) across the cell membrane either into or out of the cell – The cell membrane is selectively permeable • This means that certain materials are allowed to pass through the cell membrane while other materials are not Cellular Transport – Some cellular transport requires energy (active transport) and some does not require energy (passive transport) – 4 basic types of cellular transport • Diffusion (passive) • Osmosis (passive) • Endocytosis (active) • Exocytosis (active) Diffusion • Diffusion: random movement of molecules across a cell membrane from an area of a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Diffusion – Movement of molecules continues until the concentration of molecules is equal on each side of the cell membrane • This is known as equilibrium – Oxygen enters the cell via diffusion – Carbon dioxide leaves the cell via diffusion Osmosis • Osmosis: the diffusion of water across the cell membrane – Continues until equilibrium is reached • Concentration of water inside of the cell membrane is equal to the concentration of water outside of the cell membrane Endocytosis • Endocytosis: process by which cells absorb materials by surrounding them with their cell membrane – Happens with materials that are too large to pass through the cell membrane Outside of cell Inside of cell Exocytosis • Exocytosis: process by which cells release materials too large to normally pass through the cell membrane Outside of cell Inside of cell 5 Functions Necessary for Life 1. 2. Movement/locomotion Ability to respond to environment – – 3. Stimulus and response Cat hears the sound of the can opener (stimulus) and comes running for food (response) Use energy – 4. All cellular functions require energy Growth and development – – 5. Grow in size Develop new characteristics over their lives (ability to walk) Ability to reproduce – Replace individuals who die