* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
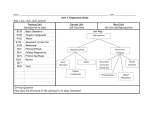
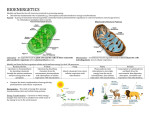
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration CH7: Cellular Respiration pg 131 Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Cellular Respiration • All living organisms go through cellular respiration. – Series of chemical reactions to make ATP from glucose Equation for Photosynthesis • 6CO2 + 6H2O + pigment + sunlight C6H12O6 + 6O2 Equation for Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 • There are 2 scenarios – Aerobic (with oxygen) – Anaerobic (without oxygen) • Anaerobic – Glycolysis (only method for some prokaryotes) • Occurs in cytoplasm • Fermentation allows for this process to keep going • 2 ATPs are made Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration • Occurs in the mitochondria • Kreb’s cycle • Electron Transport Chain Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Glycolysis • Series of chemical reactions that take place in the cytoplasm and does not need oxygen to work. • In glycolysis, enzymes break down one of glucose into two pyruvate/pyruvic acid molecules. *Glue glycolysis illustration into notes Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Glycolysis, pg 133 • Step 1, Breaking Down Glucose – Glucose is converted back into 2 - G3P (3 carbon molecule). Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Glycolysis • Step 2 and Step 3, NADH and Pyruvate – Each of the G3P go through a series of chemical reactions • Converted into Pyruvate (pyruvic acid) – 2 molecules NADH are created • Important because NADH are Hydrogen ion/proton and e- carriers Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Glycolysis Glycolysis produces 2 ATP • with O2 it also produces 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvates Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Fermentation (anaerobic process) pg 134 • To make ATP during glycolysis, NAD+ is converted to NADH. – Organisms must recycle NAD+ to continue making ATP through glycolysis. • The process in which carbohydrates are broken down in the absence of oxygen is called fermentation. – Beneficial because it allows glycolysis to continue supplying a cell with ATP in anaerobic conditions. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Pathway Lactic Acid Fermentation Section 3 Reaction PYRUVIC ACID + NADH LACTIC ACID + NAD+ *occurs in muscle cells for short term energy production, also used in the production of foods ex. yogurt, Kim chi, sauerkraut Alcoholic Fermentation PYRUVIC ACID + NADH ALCOHOL+ CO2 + NAD+ *occurs in yeast cells and is used in the production of beer, wine and bread Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Two Types of Fermentation Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration illustration Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Aerobic Respiration • 1st stage is the Krebs cycle – a series of reactions that produce electron carriers • (NADH and FADH2) • 2nd stage electron transport chain takes place in the inner membranes of mitochondria – ATP synthase are located here • Up to 36 ATP molecules can be produced from one glucose molecule in aerobic respiration. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Kreb’s Cycle • Pyruvate (from glycolysis) is broken down and combined with other carbon compounds creating CoA. – Releasing CO2 – 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Electron Transport Chain • Takes place in the inner membranes of mitochondria – ATP synthase are located here • NADH and FADH2 from the Krebs cycle – transfer energy in the form of e- and H+ into the electron transport chain. • e- are used to pump the H+ across the membrane to create a concentration gradient Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Electron Transport Chain ATP Production • Hydrogen ions diffuse through ATP synthase, providing energy to produce several ATP molecules from ADP. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 The Role of Oxygen • At the end of ETC – the e- combines with an oxygen atom and two hydrogen ions to form two water molecules. • If oxygen is not present, – the electron transport chain stops, because hydrogen has no where to go. – the electron carriers are not recycled, so the Krebs cycle also stops Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 3 Summary Cellular Respiration Reactants Products Location Gycolysis Glucose, 2 ATP 2 Pyruvates, 2NADH, 4 (2) ATP Cytoplasm Krebs Cycle 2 AcetylCoA (CoA) CO2, 6NADH, 2FADH2 ,2ATP Matrix of Mitochondria ETC 6 NADH, 2FADH2, O2 34 ATP, H2O, 6NAD, 2FAD Inner Mitochondrial Membrane