* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download temporal lobe
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
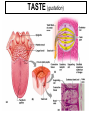
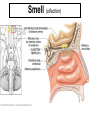
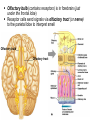
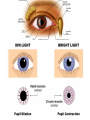
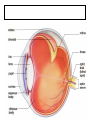
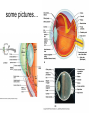
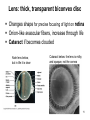
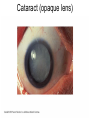
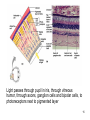
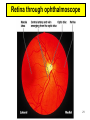
The Special Senses 1. Taste (gustation) parietal lobe (sensory area) & temporal lobe (limbic system) tongue chemical senses 2. 3. 4. 5. Smell (olfaction) Vision Hearing & Equilibrium What about Touch?...... temporal lobe (limbic system) nose eye occipital lobe hearing temporal lobe equilibrium cerebellum ear skin parietal lobe What about Touch.....? (Not really a SPECIAL sense) The sense of touch is part of the General somatic senses____ This topic deals with the Special category of the two left sensory boxes TASTE (gustation) Smell (olfaction) Olfactory bulb (contains receptors) is in forebrain (just under the frontal lobe) Receptor cells send signals via olfactory tract (or nerve) to the parietal lobe to interpret smell Olfactory bulb__ _______Olfactory tract Vision Vision is the dominant sense in humans 70% of sensory receptors in humans are in the eyes 40% of the cerebral cortex is involved in processing visual information The eye (or eyeball) is the visual organ Lies in bony orbit Surrounded by a protective cushion of fat 6 8 some pictures… 9 Chambers and fluids (see previous pics) Vitreous humor in posterior segment Jellylike Forms in embryo and lasts life-time Anterior segment filled with aqueous humor – liquid, replaced continuously Anterior chamber between cornea and iris Posterior chamber between iris and lens Glaucoma when problem with drainage resulting in increased intraocular pressure 10 Lens: thick, transparent biconvex disc Changes shape for precise focusing of light on retina Onion-like avascular fibers, increase through life Cataract if becomes clouded Note lens below, but in life it is clear Cataract below: the lens is milky and opaque, not the cornea 11 Cataract (opaque lens) The eye is an optical device: predominantly the lens (to a lesser degree, not shown here, the cornea also) Note: images are upside down and reversed from left to right, like a camera a. Resting eye set for distance vision: parallel light focused on retina b. Resting eye doesn’t see near objects because divergent rays are focused behind retina Lens accommodates (becomes rounder) so as to bend divergent rays more sharply, thereby allowing convergence on the retina c. Retina: develops as part of the brain Remember the 3 layers of the external eye? 1. (outer layer) Fibrous: dense connective tissue Sclera – white of the eye Cornea 2. (middle layer) Vascular: uvea Choroid – posterior, pigmented Ciliary body Iris 3. (inner layer) Sensory Retina and optic nerve Retina is 2 layers Outer thin pigmented layer: Melanocytes (prevent light scattering) Inner thicker neural layer Plays a direct role in vision Three type of neurons: 1. Photoreceptors 2. Bipolor cells 3. Ganglion cells 14 Light passes through pupil in iris, through vitreous humor, through axons, ganglion cells and bipolar cells, to photoreceptors next to pigmented layer 15 Photoreceptor neurons signal bipolar cells, which signal ganglion cells to generate (or not) action potentials: axons run on internal surface to optic nerve which runs to brain *Know that axons from the retina form the optic nerve, CN II 16 Photoreceptors: 2 types Rod cells Only black and white and not sharp Cone cells High acuity in bright light Color vision 3 sub-types: blue, red and green light cones One of the Ishihara charts for color blindness Commonly X-linked recessive: 8% males and 0.4% females 18 19 If you want more detail, it’s fascinating… 20 Retina through ophthalmoscope 21 Green is area seen by both eyes, and is the area of stereoscopic vision Visual pathways At the optic chiasm, nerve fibers from each eye cross to the opposite side. Optic tracts travel to and terminate in the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe. Left half of visual field perceived by right cerebral cortex, and vice versa. 22 Terminology, remember… Optic – refers to the eye Otic – refers to the ear Getting eyedrops and ear drops mixed up is probably not a good idea 23 The Ear Parts of the ear Outer (external) ear Middle ear (ossicles) for hearing) Inner ear (labyrinth) for hearing & equilibrium 24 Sound in external acoustic meatus hits tympanic membrane (eardrum) – it vibrates Pressure is equalized by the pharyngotympanic tube (AKA eustachian or auditory tube) 25 TM causes ossicles in air filled middle ear to move: Malleus (hammer) Incus (anvil) Stapes (stirrup) These are 3 of the smallest bones of the body Ossicles articulate to form a lever system that amplifies and transmits the vibratory motion of the TM to fluids of inner ear cochlea via oval window 26 Inner ear = bony “labyrinth” of 3 parts 1. Cochlea - hearing 2. Vestibule - equilibrium 3. Semicircular canals equilibrium In petrous part of the temporal bone Semicircular canals____ Filled with perilymph and endolymph fluids Vestibule___________ Cochlea_______________________ 27 Equilibrium pathway Via vestibular nerve branch of VIII (Vestibulocochlear n.) to the brain stem Only special sense for which most of the information goes to lower brain centers 28 Vestibule contains utricle and saccule Each contains a macula Senses static equilibrium and linear acceleration of the head (not rotational movements) Tips of hairs imbedded in otolithic membrane (calcium carbonate “stones”) Vestibular nerve branches of VIII (Vestibulocochlear n.) 29 Semicircular canals Each of the 3 lies in one of the 3 planes of space Sense rotational acceleration of the head Duct with ampulla housing a small crest: crista ampulla Hairs project into jellylike cupula & basilar cells synapse with fibers of vestibular nerve 30 VIII Vestibulocochlear nerve 31