* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 2 A - Kcse Online
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
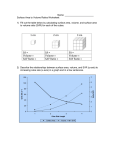
BUTERE EAST ZONE EVALUATION TEST BIOLOGY 231/2 MARKING SCHEME 1. (a) (i) Sweep net; (b) Pouter; (b) (i) Synthesis of ribosomes; (ii) Destroy worn out cell organelles/cells; (iii) Synthesis of protein; (c) Plant cell Animal cell - Has cell wall; - No cell wall; - Store carbohydrates inform of starch; - Stores carbohydrates in form of glycogen; - Regular in shape; - Irregular in shape; - Has a peripheral nucleus; - Ha a centrally placed nucleus; - Large central vacuole; - Small vacuoles scattered in the cytoplasm; - Some have chloroplasts; - No chloroplasts; 2. (a) (i) A- Root nodules; D – Root hairs; (ii) – Nitrates; (iii) – It’s the conversion of free nitrogen in air into nitrates; (b) (i) – It’s the linear flow of energy through different trophic levels in an ecosystem; (ii) – Primary consumers; (iii) – Pyramid of numbers – to be drawn to scale; Scale 1 cm rep. 100 organisms. Nile perch (100) Tilapia (300) Planktonic algae (1000) 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 (c) – There is gradual decrease in numbers due to energy loss through respiration, defeacation, urination; 3. (a) – Homodont – dentition with one type and shape of teeth; - Heterodont - dentition with different types and shape of teeth; (b) (i) 30 teeth; (ii) - Herbivorous/herbirory; (iii) - Lack upper incisors and canines; (c) – Mortar tooth – has broad surface with cusps; ©2015 BTR east f3 1 Biology 231/2 Function: Increases surface area for grinding; - Carnassial tooth – sharp edge for shearing; - Slicing flesh/for crushing bones, Diagram – double walled. 4. (a) (i) - Well cell membrane. (1 mk) Labeling – cell membrane - vacuole (2 mks) – The salt solution was hypertonic to the cell sap; the vacuole lost water to the solution by (ii) osmosis; hence reducing in size; (iii) - Plasmolysis; 5. (a) - Scientific system of giving organisms two names; Generic and specific names; (b) - Identification/placing them in their correct groups; - To understand the evolutionary relationship between organisms; - To arrange information about living organisms in an orderly manner for easy study/avoid confusion; (c) Insecta Arachinida - 3 pairs of limbs; 4 pairs of limbs; - 3 body parts; 2 body parts; - Gaseous exchange through Gaseous exchange through book lungs; tracheal system; 6. (a) Scale – 1 x 2 = 2 mks Plotting – 1 x 2 = 2 mks Curves – ½ x 2 = 1 mk Axes – ½ x 2 = 1 mk Identification = ½ x 2 = 1 mk (Total = 7 mks) (b) (i) – Frog; - Body temperature increases with increase in environmental temperature; frogs are ectotherms/poikilothem; hence cannot control their body temperature by physiological means; (ii) Student; (c) (i) – High osmotic pressure stimulates the hypothalamus /osmoreceptor cells that send an impulse to the pituitary gland to secrete ADH; which is transported to the kidney tubules; making them more permeable to water; more water is reabsorbed into the blood stream lowering the osmotic pressure; back to normal; ©2015 BTR east f3 2 Biology 231/2 (ii) – Deamination – the removal of amino group from an amino acid in the orinthine cycle; 7. (a) - The root hairs grows between the soil particles surrounded by a film of water/soil solution; The sap in the root hair has higher osmotic pressure than the soil solution; Water is drawn into the root hair by osmosis; This dilutes the cell sap in epidermal cell; relative to the sap in the adjacent cortical cells; Because of this, water moves into the adjacent cortical cells; until it reaches the xylem vessels; Within the leaf cells; some water is used in the manufacture of food; and some vapourises when the temperatures are high; gets into the intercellular air spaces; and diffuse out of the leaf; through the stomatal opening; into the atmosphere; in a process called transpiration; (Total 17 mks) (b) Mechanisms of translocation of manufactures food. - Active transport; - Mass flow; - Surface spreading; - Cytoplasmic streaming; (Any three correct points = 3 mks) 8. (a) Characteristics of respiratory surfaces. - Thin epithelium for faster diffusion of gases; - Folded or branched creating large surface are for rapid diffusion of gases. - Have rich supply of blood capillaries for fast transport of gases to and from tissue; - Have moist surfaces to enable diffusion of gases (1 mk each = 4 mks) (b) Adaption of mammalian lungs to their functions; - Lungs are surrounded by a 2 – layered membrane called pleural membrane; which protect the lungs from mechanical damage; between the two layers is a cavity called pleural cavity; filled with pleural fluid; that lubricates lungs; protecting it from friction/abrasion; by inner walls of the thorax as they are inflated and deflated; The lungs have a dense network of blood capillaries; that increase surface area; over which gases diffuse for transportation; The lungs have numerous air sacs(alveoli); that store air, and provide surface over which gaseous exchange takes place; The lungs are elastic; hence expand and contract to hold and expel large volume of air; The lungs are located in the rib cage; that cushions them from mechanical damage; Total: 17 points Max: 16 mks) ©2015 BTR east f3 3 Biology 231/2