* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System aka Circulatory System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
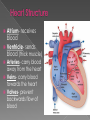
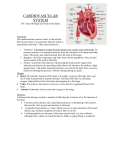
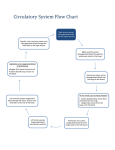
Cardio- means heart Vascular- means blood vessels Aka Circulatory System because its job is to circulate blood throughout the body. Blood carries many materials including: › Nutrients from food › Oxygen from the lungs › Wastes from cells › Hormones (chemical messages) Heart- main organ of the cardiovascular system › made mostly of cardiac muscle tissue › Right side pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs (left side in pictures) › Left side pumps oxygen rich blood to the body (right side in pictures) › 4 chambers: atrium = upper, ventricle = lower › One-way valves separate the chambers so blood can’t flow backwards Atrium- receives blood Ventricle- sends blood (thick muscle) Arteries- carry blood away from the heart Veins- carry blood towards the heart Valves- prevent backwards flow of blood Arteries- bring blood away from heart › Thick, muscular walls to help pump and withstand pressure. › Typically carry oxygenated blood. › EXCEPTION: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood away from heart to the lungs. Capillaries- exchange materials with cells › Extremely thin-walled blood vessels. › Exchange O2 and nutrients for CO2 and wastes. Veins- bring blood towards the heart › One-way valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards › Typically carry deoxygenated blood. › EXCEPTION: Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood towards the heart from the lungs. Systemic Circulation- blood flow between the heart and the body. › Purpose: to deliver O2 and nutrients and pick up wastes from body cells › Left ventricle (larger to pump to entire body) Pulmonary Circulation- blood flow between the heart and the lungs. › Purpose: to replenish O2 and drop off CO2 at lungs. › Right ventricle Cardiovascular problems affect your entire body. › Atherosclerosis (narrowing of blood vessels) › Hypertension (high blood pressure) › Heart attack & stroke- blood flow to heart or brain is blocked Causes: smoking, high cholesterol, stress, physical inactivity, heredity Eat healthy and get plenty of exercise to keep cardiovascular system healthy