* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
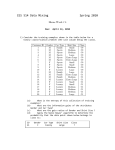
Biology Final Review –07 Intro and taxonomy 1. six steps of the scientific method 2. 7 taxa in order from largest to smallest 3. Define binomial nomenclature, specify who developed it 4. An example of an organism in each of the 7 kingdoms Ecology 4. Define: producer, consumer, decomposer, detrivore, examples of each 5. Trophic levels, relative # of organisms at each level 6. Energy loss from one trophic level to the next 7. Define population, community, types of symbiosis (give examples), carrying capacity 8. Define species diversity, where is it at a maximum? Why is it important? 9. Describe major aquatic and terrestrial biomes, know where they occur and what organisms live there 10. Predator / prey relationships, trends in relative population growths Cytology 11. Cell theory (3 parts) 12. Cellular organelles and their f(x)s 13. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes 14. Calculation of microscope magnification 15. Transport (osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, equilibrium, active vs. passive, exocytosis, endocytosis Cell Growth and Division 16. Define the cell cycle .Why must a cell divide (specifically)? What happens during the different parts of interphase? 17. Purpose, names and events of phases, and products of mitosis. 18. What kinds of cells often divide? Rarely divide? Genetics 19. Who was the father of genetics? 20. Define: dominance, recessiveness, phenotype, genotype, Punnett square, gamete, hybrid, homozygous, heterozygous, segregation, haploid, diploid, homologous chromosomes, gene, trait, sex-linked genes, mutation 21. In what sex do sex-linked disorders usually appear? 22. Probability- define, 3 facts 23. Be able to use a Punnett square to do a single-factor cross and determine the phenotypic and genotypic ratios. 24. Know about the following human genetic disorders: Huntington’s, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, hemophilia, sickle-cell anemia – symptoms, treatments, prognoses. 27. What are amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling, and how do they differ from each other? 28. Define meiosis, its purpose, and its products. Biotechnology 29. What is the Innocence Project? 30. What specific fluids/tissues can be used for DNA analysis? 31. Define: cloning, genetic engineering, gene therapy, xenotransplatation. DNA and Protein Synthesis 32. Know the structure of DNA, the N-bases, which goes with which, building blocks of DNA, building blocks of proteins, nucleotide structure. 33. What are the steps of DNA replication? What does complementary mean? 34. Which N-base replaces thymine in RNA? 35. Define transformation, transcription, translation. 36. Know the steps of protein synthesis and where they take place. 37. Define bacteriophage, include structure. Why was this useful in finding the structure of DNA? 38. What does a codon code for? 39. Upon the sequence of what does the genetic code depend? Microbiology (Viruses, Bacteria, Protists,) 40. Know which of the following is a virus, a bacterium, or a protist or a fungus: Giardia, malaria, tetanus, rabies, tuberculosis, influenza, Ebola, Common cold, Bubonic plague, salmonella, African sleeping sickness, strep, amoebic dysentery, HIV 41. Know the structure of a virus. Define. Are they alive? Why or why not? 42. Know the lytic vs. the lysogenic cycle 43. Define retrovirus and give an example 44. How are viral diseases transmitted? 45. What are two phyla of bacteria and where are they generally found? 46. How is bacteria helpful? Harmful? 47. Define binary fission, conjugation, budding. 48. Know the shapes and groupings of bacteria 49. Know the f(x)s of the major organelles of protists, and give an example of a protist that has each organelle. Fungi 50. Know what caused the potato famine of 1845-47. 51. Define and give f(x)s of hyphae, mycelium, lichen, absorption of nutrients, mushroom, yeast, fungal cell wall composition, mycorrizhae. 52. List three ways fungi are useful to us. 53. List and identify two common human diseases caused by fungi. Plantae 54. Dominant generations of mosses and ferns. Define sori. 55. Why can mosses never be tall? 56. What structures do vascular plants have? 57. What are two types of vascular tissue and their f(x)s. 58. Define and give examples of gymnosperms, angiosperms, cycads, conifers. 59. What are stomata, what are their f(x)s, and what cells border them? 60. Define cuticle. Give f(x). 61. Know three differences between monocots vs. dicots. Give examples of each. Invertebrates 62. Phylum Porifera : what belongs in this group, Osculum, ostia, 7 essential life f(x)s for a sponge 63. Phylum Cnidaria : what belongs in this group, 2 body forms, 7 essential life f(x)s for a jelly fish, nematocyst, type of larvae 64. Phylum Platyhelminthes : common name of this group, what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s for a flatworm 65. Phylum Nematoda : common name of this group, what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s for a roundworm 66. Phylum Molluska: common name of this group, what belongs in the 3 classes in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s for a Gastropod, Bivalve, & Cephalopod, 67. Phylum Annelida : common name of this group, what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s for earthworms vs. leeches 68. Phylum Arthropoda: Spiders, ticks, mites 7 essential life f(x)s for earthworms vs. leeches 69. Phylum Arthropoda: Crustaceans, 7 essential life f(x)s 70. Phylum Arthropoda : Centipedes, millipedes & insects, 7 essential life f(x)s 71. Phylum Echinodermata: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s for sea stars, 3 reasons they are similar to chordates 72. Invertebrate Chordates: two examples, 4 trade marks of chordates, 7 essential life f(x)s, Subphylum Vertebrata: Vertebrates : Study all materials you have received!! 73. Agnatha: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s 74. Chondrichthyes: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s 75. Osteichthyes: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s 76. Class Amphibia: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s 77. Class Reptilia: what belongs in this group 7 essential life f(x)s 78. Class Aves: what belongs in this group,7 essential life f(x)s 79. Class Mammalia: what belongs in this group, 7 essential life f(x)s, 4 characteristics of mammals, type of teeth, function of the cerebrum, developmental differences between monotremes, marsupials, & placental mammals, characteristics of & what belongs in each of the 15 orders we studied,