* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS: THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
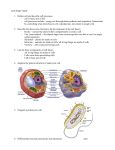
CELLS: THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Some Cell Fun Facts You can grow heart cells in a petri dish. Humans have an estimated 10 trillion cells. The largest known cell is an unfertilized ostrich egg cell. The word cell comes from the Latin word cellula, meaning, “small room”. One single cell contains two meters of DNA. Humans shed and re-grow outer skin cells about every 27 days. Cells Discovered in 1665 Why didn’t we know about cells before this? Robert Hooke’s microscope: Section One: The Diversity of Cells Part 1:The Discovery of Cells 1665 Robert Hooke First person to describe cells Also looked at feathers, fish scales, and eyeballs of house flies Mostly looked at plants and fungi (these things have cell walls)- makes them easy to see 1673 ANTON van LEEUWENHOEK Found cells in other organisms…. SAW “ANIMALCULES” IN POND SCUM ALSO SAW BLOOD CELLS AND BACTERIA for the first time 200 Years Later… 1838 Matthias Schleiden, a German scientist said….all plant parts are made of cells One year later, Theodor Schwann, a German scientist that studied animals stated that all animal tissues are made of cells 1858 Rudolf Virschow Said that all cells form only from other cells THE CELL THEORY: 1. ALL ORGANISMS ARE ONE OR MORE CELLS 2. CELL IS THE UNIT OF ALL LIFE 3. All cells come from existing cells 4 Parts found in all Cells 4. Cytoplasm- the fluid 1. Cell membrane-outer covering 2. Organellessmall bodies in the cytoplasm 3. DNA (genetic material) inside a cell along with all the cell’s contents All cells have a … Small size Smallest=bacteria Largest=ostrich egg how big animation Two Kinds of Cells: 1. Cells without a nucleus Called Prokaryotic cells These can be either: bacteria or archaea Are super small in size 2. Cells with a nucleus Called Eukaryotes (these are the cells in plants, animals and fungi) PROKARYOTIC CELLS Bacteria, and Archaea NO NUCLEUS NO MEMBRANES AROUND ORGANELLES CIRCULAR DNA (looks a little like a rubber band) Bacteria Most common prokaryotes Smallest cells known Live almost everywhere No nucleus but DO have DNA DNA is long and shaped like a twisted rubber band (circular shaped) No membrane-covered organelles Do have ribosomes and cell wall Brainpop Archaea… Same as bacteria except: Ribosomes are different…..are more like Eukaryotic ribosomes Cell wall and cell membranes are made of different materials Many live in Bizarre environments! Ex. heat-loving, salt-loving, methane-making archaea SURFACE TO VOLUME RATIO: ORGANISMS NEED SMALL CELLS TO KEEP THE RIGHT SURFACE TO VOLUME RATIO IF A CELL GROWS TOO BIG, THERE WON’T BE ENOUGH OPENINGS IN THE SURFACE TO LET MATERIALS IN AND OUT ! EUKARYOTIC CELLS(our cells) (ALL CELLS) EXCEPT bacteria and Archaea Are 10 times bigger than bacteria Have a NUCLEUS Have MEMBRANE –COVERED ORGANELLES Have LINEAR DNA found inside a nucleus Really important cell vocab: CELLULOSE- tough stuff in plant cell walls ATP- the “energy molecule” for a cell, (is like gasoline for a car) DNA- instructions for the cell PHOSPHOLIPIDS- the stuff all membranes are made of Section 2 The Inside of a Eukaryotic Cell The “true” cell. plants animals fungi Fluency Chart… Cell wall ribosome Golgi Complex vesicle Mitochondrion plural=mitochondria Golgi Complex Cell membrane lysosome vesicle E.R. ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Plant Cells Video: CELL WALL IN PLANT CELLS (and algae) ONLY Made of a hard material called Cellulose Provides strength and support to the cell membrane When you look at dried hay, sticks and wooden boards you are seeing the cell walls of dead plant cells! PLANT CELL WALL PICTURES: CELL MEMBRANE All cells are covered by this Is formed by phospholipid molecules Allows nutrients in Allows waste products out: Cytoskeleton A web of proteins in the cytoplasm that acts as a muscle and a skeleton. It helps a cell retain its shape and moves organelles around. NUCLEUS: Library, or Town center Stores the DNA Has all the “secret info” for the organism RIBOSOMES: SMALLEST of all ORGANELLES (THE DOTS) ON THE E.R. (only organelle without a membrane) Act like factories for making proteins MITOCHONDRIA: Power plants…release energy for the cell Make the ATP Used in all cell ( activities) VACUOLE: Is really big in plant cells Small in animal cells Serves as a water storage compartment CHLOROPLASTS:(plant cells only!) •Contains chlorophyll •Captures sunlight to make food (sugar) used by mitochondria •Makes plants appear green : GOLGI COMPLEX: FedEx Delivery Gets rid of things inside the cell Shipping and Handling Cellular Digestion… LYSOSOMES: Contain digestive enzymes Clean-up/ destroy cell waste, sometimes called the recycling center Can act as security to protect the cell from invaders Sanitation company? Mainly in animal cells ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Post office, delivery system, tunnel system Makes lipids for membranes, processes and transports proteins CELL: ER Cytoplasm VESICLES: Membrane –covered compartments inside the cell Animal cells: human cheek cells Scientists believe that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as a prokaryotic cell that was “eaten” by larger cells. They ended up surviving inside. EVIDENCE? •Both have two membranes •Have a) ribosomes and b) circular DNA •Same size as bacteria •Divide like bacteria Sec.3: The Organization of Living Things…(Small to big) CELLS TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEMS ORGANISM Organism Anything that can perform life processes by itself Euglena: Organisms can be: Unicellular-(single celled) Multicellular- (consists of many cells) Larger size Longer life Specialization Each type of cell has a special job Makes the organism more efficient Structure and Function In an organism, structure and function are related. Example: Alveoli air sacs in the lungs: See fig. 4 p.79 End of Ch 3 Cells: The Basic Units of Life