* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
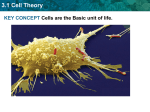
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory Learning Targets I can describe developments that led to the cell theory. I can differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. • More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. • More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. • The cell theory is a unifying concept of biology. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. cytoplasm Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. nucleus cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. nucleus • Prokaryotic cells do not have membranebound organelles. organelles cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. nucleus organelles cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. nucleus • Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles. organelles cell membrane cytoplasm 3.1 Cell Theory Checkpoint 1. Compare and Contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. 2. Suppose a certain poison kills human cells by blocking pores in the nuclear membrane. Explain why it would or would not kill bacteria.