* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
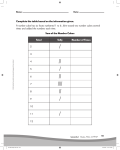
Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology Why Smaller Cells? – Comparing Surface Areas Laboratory Section 2.4 Pages 38-39 All plants and animals are composed of small cells. Why is there a limit to cell size? What do cells do to survive? Cells need a constant supply of nutrients, water and oxygen. As well, wastes must be removed from the cell. The processes of “entering and exiting” a cell are (1) osmosis, (2) diffusion and (3) active transport Cells must communicate internally. The nucleus must efficiently receive signals from the surrounding environment, and then, quickly communicate messages to other cell organelles to react to changes in the environment. An example is exposure to the Sun. For most people, exposure to the Sun makes the skin darker. How? Sunlight triggers a chemical message in the cell that travels to the nucleus. The nucleus decodes the information and instructs the ribosome to produce melanin. The melanin blocks sunlight to prevent sunlight from damaging the cell. The melanin is the tanning of the skin. Cells can be different sizes…depending on their function. Cells in fat tissue are bigger than cells in muscle tissue. Why? HINT: Muscle cells constantly active. Purpose To understand surface area To understand that the size of the cell is important in its efficiency when transporting information, water, oxygen, nutrients and waste To make a prediction whether many small cells or one large cell would be more efficient exchanging nutrients and waste Hypothesis Materials 8 sugar cubes Ruler Calculator Marker NOTE: Each cube represents a single cell Methods 1. Using a ruler, measure the length and width of a sugar cube in millimetres 2. Repeat this measurement for each face of the sugar cube marking each face of the sugar cube after it is measured. The mark will prevent you from measuring the same face again 3. Calculate TOTAL SURFACE AREA for one cube. To do this, calculate the surface area for each face (length X width), and then, find the sum of all surface areas 4. Calculate the TOTAL SURFACE AREA for eight sugar cubes. The easiest method would be to assume all sugar cubes are similar in size and multiply the total surface area for one cube by eight 5. Arrange the eight sugar cubes so a large cube is formed. This block represents one large cell 6. Measure the length and width of the large cube. 7. Calculate the TOTAL SURFACE AREA of the large cube (…again length X width). 8. Compare the surface area of the eight individual cubes with the one large cube. Which has the larger TOTAL SURFACE AREA? 9. From your results, which configuration (eight small cells or one large cell) has more cell membrane for nutrients and waste to pass through? What do your findings suggest about the size of a cell? Questions 1. Muscle cells are highly active. They tend to be small. From your findings, suggest one reason for their relatively small size. 2. Fat cells are bigger than muscle cells. By comparing the functions as a fat cell to a muscle cell can you explain why a fat cell is bigger? 3. Why is surface area important to a cell? Provide one idea with your answer 4. Which size of cell is more efficient at transporting message from the nucleus to the other cell organelles? Provide one reason with your answer. 5. A message from the surroundings takes longer to reach the nucleus and it takes longer for instructions from the nucleus to reach other parts of the cell if the cell is big. When you tan, the Sun makes your skin darker. This occurs because your skin cells produce the Melanin protein to block sunlight. Skin cells are typically small. Why? Provide one reason with your answer. 6. Which cell has the greater surface area they have similar volumes. (a) A cell shaped like a sphere or a cell shaped like a cube? (b) A cell with a smooth surface or one of the many projections?










![[30] Data preprocessing. (a) Suppose a group of 12 students with](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000372524_1-ddd599b65768a709331a44314283ca76-150x150.png)










