* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SQL Server Analysis Services
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
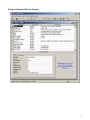
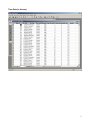
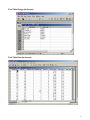
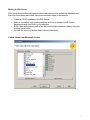
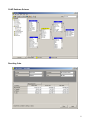
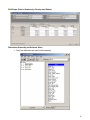
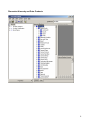
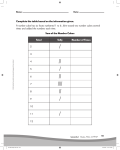
SQL Server Analysis Services Microsoft® SQL Server™ 2000 Analysis Services is a middle-tier server for online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining. The Analysis Services system includes a server that manages multidimensional cubes of data for analysis and provides rapid client access to cube information. Analysis Services organizes data from a data warehouse into cubes with pre-calculated aggregation data to provide rapid answers to complex analytical queries. Analysis Services also allows you to create data mining models from both multidimensional (OLAP) and relational data sources. You can apply data mining models to both types of data. PivotTable® Service, the included OLE DB compliant provider, is used by Microsoft Excel and applications from other vendors to retrieve data from the server and present it to the user, or create local data cubes for offline analysis. Multiple Data Storage Options Analysis Services offers three storage modes for dimensions, partitions, and cubes: Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) The underlying data for a cube is stored along with aggregation data in a highperformance multidimensional structure. MOLAP storage provides excellent performance and data compression. Relational OLAP (ROLAP) The underlying data for a cube is stored along with the aggregation data in a relational database. ROLAP storage enables you to take advantage of your investment in relational technology and enterprise data management tools. Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP) The underlying data for a cube is stored in a relational database and the aggregation data is stored in a high-performance multidimensional structure. HOLAP storage offers the benefits of MOLAP for aggregations without necessitating duplication of the underlying detail data. Linked Cubes A cube can be stored on a single server and referenced as a linked cube on other servers. Users connected to any of these servers can then access the cube. This approach avoids the more costly alternative of storing and maintaining copies of a cube on multiple servers. Linked cubes make it possible for you to create, store, and maintain a cube on one Analysis server while providing access to the cube from multiple Analysis servers. Linked cubes facilitate cube security and reduce storage and maintenance requirements. 1 SQL Server Analysis Manager Console Microsoft Access Database (Origin of Data) 2 Design of Product Table (in Access) 3 Product Data (in Access) 4 Time Data (in Access) 5 Fact Table Design (in Access) Fact Table Data (in Access) 6 Moving to SQL Server SQL Server Analysis Services requires data to be retrieved from an existing database and then form the schema and cubes. Here are some basic steps of the process: Create an OLAP database in the SQL Server Make a connection to an existing database such as an Access or SQL Server database through the DSN in your computer. Build a data cube schema (with a fact table and multiple dimension tables) using the existing linked tables. Process the cube to populate data in various hierarchies. Linked Tables from Microsoft Access 7 OLAP Database Schema Resulting Cube 8 Browsing the Cube (Drill-Down) Drill-Down (Product and Product Category by Country) 9 Drill-Down (Sale in Quarters by Country and States) Dimension Hierarchy and Schema: Store Only few attributes are used in the hierarchy 10 Dimension Hierarchy and Data: Products 11