* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
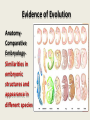
Evolution by Means of Natural Selection Evolution 1. 2. The process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. A change in the genes over time. Old (bad) Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste Lamarck (early 1800’s) proposed: “The inheritance of acquired characteristics” He proposed that by using or not using its body parts, an individual tends to develop certain characteristics which it passes on to its offspring. “The Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics” • Example: A giraffe acquired its long neck because its ancestor stretched higher and higher into the trees to reach leaves, and that the animal’s increasingly lengthened neck was passed on to its offspring. Charles Darwin Influenced by Charles Lyell who published “Principles of Geology” in 1830-1833. This publication led Darwin to realize that natural forces gradually change Earth’s surface and that the forces of the past are still operating in modern times. Charles Darwin Darwin set sail on the H.M.S. Beagle (1831-1836) to survey the south seas (mainly South America and the Galapagos Islands) and to collect plants and animals. On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed species that lived no where else in the world. Charles Darwin • Wrote “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection” in 1859 Two main points: 1. Species were not created in their present form, but evolved from ancestral species. 2. Proposed natural selection as the way evolution takes place. Natural Selection • More individuals are born than can possibly survive. • This creates competition for resources. • There is always variation among individuals for any particular trait. Natural selection cont. • These traits are heritable. They are passed from parents to their offspring. • Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. • These traits accumulate as adaptations. Adaptation Any trait that helps an individual survive in its environment. In other words… There is a struggle for existence in which individuals who are better suited to the environment survive and reproduce at higher rates. Survival of the fittest Descent with Modification Artificial Selection Darwin used selective breeding to support his idea. Selective breeding- when people choose individuals with desired traits to reproduce. Question: How many species of dog are there? Answer: 1, Dog breeds are a human creation. Evidence of Evolution 1. Biogeography 2. Adaptations 3. Fossil Record 4. Anatomy 5. Biochemistry Evidence of Evolution Biogeography- the distribution of life around the world. Evidence of Evolution Adaptations1. Structural adaptations-wings, claws, etc. 2. Camouflage 3. Mimicry Adaptations 4. Convergent evolution-species that live in similar environments or that exploit similar resources develop similar adaptations. *Analogous structures are evidence of this! Adaptations 5. Divergent evolution- species that become isolated from reproducing together develop different adaptations and become different species. *Homologous structures are evidence of this! Evidence of Evolution The fossil recordA history of life on earth Evidence of Evolution Anatomyhomologous structures- structures that share a common ancestry but serve different functions Evidence of Evolution • Anatomy• Analogous Structures- structures that DO NOT share a common ancestry but have similar structure and function Evidence of Evolution AnatomyComparative EmbryologySimilarities in embryonic structures and appearance in different species Evidence of Evolution AnatomyVestigial structures Structure that serves no useful function in an organism but was useful for an ancestor. Evidence of Evolution Biochemistry- All life on earth uses DNA to store and transmit genetic information. Species A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. Population A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area. Gene pool All of the genes (alleles) in a population. Genetic Variation 2 main sources: 1. Mutation- change in the DNA 1. Sexual reproduction results in genetic “shuffling.”