Geology and Geophysics (GEOS)
... Promote a broader understanding of deep time through an examination of life and environments during the Mesozoic, or "Age of Dinosaurs." Discussions and exercises will focus on major events and processes that shaped the physical environments of the Mesozoic, such as the formation and break up of con ...
... Promote a broader understanding of deep time through an examination of life and environments during the Mesozoic, or "Age of Dinosaurs." Discussions and exercises will focus on major events and processes that shaped the physical environments of the Mesozoic, such as the formation and break up of con ...
Exploring Geology: What-To-Know List
... List the main characteristics of obsidian, pumice, scoria, tuff, breccia, and pegmatite, and indicate where each of these rock types fits into an igneous classification system based on composition. Summarize the main minerals that are present in felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic rocks. ...
... List the main characteristics of obsidian, pumice, scoria, tuff, breccia, and pegmatite, and indicate where each of these rock types fits into an igneous classification system based on composition. Summarize the main minerals that are present in felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic rocks. ...
View - Mid Wales Geology Club
... 1820s.9 Fossils were common in younger rocks but during his work in the mid 1820s he thought the older rocks ‘below the region of animal life’ and did not even look for fossils.10 When the two men entered Wales there was no concept of the movement and collision of continents, and no understanding of ...
... 1820s.9 Fossils were common in younger rocks but during his work in the mid 1820s he thought the older rocks ‘below the region of animal life’ and did not even look for fossils.10 When the two men entered Wales there was no concept of the movement and collision of continents, and no understanding of ...
Geological Society of America Bulletin
... belts. Magmatism during each of these phases produces spatially and temporally associated, mafic-ultramafic to highly evolved rock assemblages. These rock units, which have varying internal structures, geochemical affinities, and age ranges, and originally formed in different geodynamic settings, co ...
... belts. Magmatism during each of these phases produces spatially and temporally associated, mafic-ultramafic to highly evolved rock assemblages. These rock units, which have varying internal structures, geochemical affinities, and age ranges, and originally formed in different geodynamic settings, co ...
Evolution Unit Practice Test
... 55. Homologous structures are evidence for Darwin’s idea that all life on Earth is connected through _________________________. 56. Charles Darwin concluded that the distribution of living and extinct ____________________ around the world could provide evidence of evolution. 57. Geologists use _____ ...
... 55. Homologous structures are evidence for Darwin’s idea that all life on Earth is connected through _________________________. 56. Charles Darwin concluded that the distribution of living and extinct ____________________ around the world could provide evidence of evolution. 57. Geologists use _____ ...
FREE Sample Here
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Ocean crust is generally lower in elevation ________. A) averaging about 380 metres below sea level B) entirely because of the great weight of the overlying sea water C) and contains prominent r ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Ocean crust is generally lower in elevation ________. A) averaging about 380 metres below sea level B) entirely because of the great weight of the overlying sea water C) and contains prominent r ...
`granitic` laver of the crust in the southern norwegian precambrian
... more obscure but whose layering is most likely inherited from original supracrustal rocks constitute the predominant rock type at deeper levels. In central Telemark, DoNs (1960, p. 56) has described the contact between the supracrustal rocks and the underlying granitic gneisses as being gradational ...
... more obscure but whose layering is most likely inherited from original supracrustal rocks constitute the predominant rock type at deeper levels. In central Telemark, DoNs (1960, p. 56) has described the contact between the supracrustal rocks and the underlying granitic gneisses as being gradational ...
The evolving nature of terrestrial crust from the Hadean, through the
... of early crustal evolution that we think we know best branching out into the ever less well constrained. This will start on the firm ground of long-known long-lived, ancient continental crust of cratons that preserve nearly the full Archaean crustal record. Only once the processes that have shaped lo ...
... of early crustal evolution that we think we know best branching out into the ever less well constrained. This will start on the firm ground of long-known long-lived, ancient continental crust of cratons that preserve nearly the full Archaean crustal record. Only once the processes that have shaped lo ...
Geology - Archean Environment: The habitat of early life.
... a progressively degraded record with increasing age. However, it is likely that some Phanerozoic UHT granulite metamorphism rocks have not yet been exposed at Earth’s surface, leading to bias in the younger part of the record. Extrapolation back in time also raises questions about partial-to-complet ...
... a progressively degraded record with increasing age. However, it is likely that some Phanerozoic UHT granulite metamorphism rocks have not yet been exposed at Earth’s surface, leading to bias in the younger part of the record. Extrapolation back in time also raises questions about partial-to-complet ...
General Biology II
... does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, age, disability or veteran status in its programs and activities. The following person has been designated to handle inquiries regarding the non-discrimination policies: Dr. George Barnes, Vice President for Administr ...
... does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, age, disability or veteran status in its programs and activities. The following person has been designated to handle inquiries regarding the non-discrimination policies: Dr. George Barnes, Vice President for Administr ...
Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0)
... are able to carry out photosynthesis; their cells have cellulose cell walls; they store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose Examples include flowering plants, such as a cereal (for example maize), and a herbaceous legume (for example peas or beans) Animals: These are multicellular organisms; their ce ...
... are able to carry out photosynthesis; their cells have cellulose cell walls; they store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose Examples include flowering plants, such as a cereal (for example maize), and a herbaceous legume (for example peas or beans) Animals: These are multicellular organisms; their ce ...
Interactive Textbook - St. Helens School District
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Requests for permission to make ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Requests for permission to make ...
Plate Tectonics
... ■ Hands-on Activities ■ Meeting Individual Needs (Extension and Intervention) ■ Transparency Activities A teacher support and planning section including ■ Content Outline of the chapter ...
... ■ Hands-on Activities ■ Meeting Individual Needs (Extension and Intervention) ■ Transparency Activities A teacher support and planning section including ■ Content Outline of the chapter ...
Weathering
... crust and upper mantle are broken into huge slabs called plates. Forces deep within Earth cause these plates to move and change the surface. For example, most mountains form when plates come together. ...
... crust and upper mantle are broken into huge slabs called plates. Forces deep within Earth cause these plates to move and change the surface. For example, most mountains form when plates come together. ...
Why Natural Selection cannot Explain Rationality
... kinds of deviations from rationality [Khalil, 207e]. In any case, these details and debates should not influence the question pursued in this essay. Sill, what do we need to know about rationality for the purpose of this article? Briefly, there are two definitions of rationality, the “technical” and ...
... kinds of deviations from rationality [Khalil, 207e]. In any case, these details and debates should not influence the question pursued in this essay. Sill, what do we need to know about rationality for the purpose of this article? Briefly, there are two definitions of rationality, the “technical” and ...
Plate tectonics began in Neoproterozoic time
... characteristics of oceanic mantle and obviates all need for deepsourced plumes; conversely, plume theory does not explain those characteristics (Anderson, in press). Shearing also smears out deep subcontinental lithospheric mantle. Subduction did not operate during most of Precambrian time, but dela ...
... characteristics of oceanic mantle and obviates all need for deepsourced plumes; conversely, plume theory does not explain those characteristics (Anderson, in press). Shearing also smears out deep subcontinental lithospheric mantle. Subduction did not operate during most of Precambrian time, but dela ...
Geological Sciences (GSC) - University of Miami Academic Bulletin
... GSC 240. Introduction to Marine Geology. 3 Credit Hours. Learn about the origin, structure and evolution of the ocean basins and their margins, including interpretation of the paleo-archives hidden on the seafloor. The course material is necessarily broad, covering marine geography, plate tectonics, ...
... GSC 240. Introduction to Marine Geology. 3 Credit Hours. Learn about the origin, structure and evolution of the ocean basins and their margins, including interpretation of the paleo-archives hidden on the seafloor. The course material is necessarily broad, covering marine geography, plate tectonics, ...
“History of Evolutionary Thought” Game Cards: 3 pts. Darwin
... 4 pts. What is the two-word term for life being created from non-living things? 4 pts. What is the term for the theory that living things only come from other living things? (biogenesis) 5 pts. According to the most recent hypothesis, what would the first organic monomers have been? 5 pts. Name two ...
... 4 pts. What is the two-word term for life being created from non-living things? 4 pts. What is the term for the theory that living things only come from other living things? (biogenesis) 5 pts. According to the most recent hypothesis, what would the first organic monomers have been? 5 pts. Name two ...
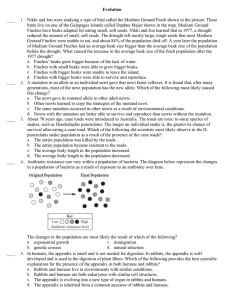
Evolution ____ 1. Nikki and Jon were studying a type of bird called
... Spines and thorns on plants look similar, and both provide protection from herbivores. However, not all plants with spines or thorns have descended from a recent common ancestor. Spines are modified leaves, and thorns are modified stems. Which of the following statements best describes how this info ...
... Spines and thorns on plants look similar, and both provide protection from herbivores. However, not all plants with spines or thorns have descended from a recent common ancestor. Spines are modified leaves, and thorns are modified stems. Which of the following statements best describes how this info ...
Chapter 10: Plate Tectonics
... the study of Earth. Graphic refers to a drawing or painting. Therefore, paleogeographic could be translated as “Old Earth Picture.” Scientists often use fossil evidence to help them develop a picture of how Earth was long ago. By examining and dating rock formations and fossils of various plants and ...
... the study of Earth. Graphic refers to a drawing or painting. Therefore, paleogeographic could be translated as “Old Earth Picture.” Scientists often use fossil evidence to help them develop a picture of how Earth was long ago. By examining and dating rock formations and fossils of various plants and ...
Evolutionary geochemical patterns of Late Cretaceous to
... crust. A detailed study of long-term subduction-related magmatism along an ∼500 km long section in the central Andean foreland may provide support for this rival hypothesis. I compiled major and trace element and Sr and Nd isotopic data for 501 samples of Andean magmatic rocks from North Chile (21–2 ...
... crust. A detailed study of long-term subduction-related magmatism along an ∼500 km long section in the central Andean foreland may provide support for this rival hypothesis. I compiled major and trace element and Sr and Nd isotopic data for 501 samples of Andean magmatic rocks from North Chile (21–2 ...
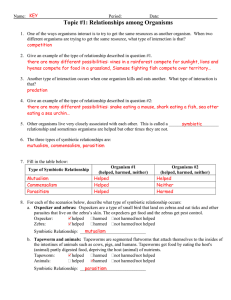
Which Symbiosis is it
... there are many different possibilities: vines in a rainforest compete for sunlight, lions and hyenas compete for food in a grassland, Siamese fighting fish compete over territory… 3. Another type of interaction occurs when one organism kills and eats another. What type of interaction is that? predat ...
... there are many different possibilities: vines in a rainforest compete for sunlight, lions and hyenas compete for food in a grassland, Siamese fighting fish compete over territory… 3. Another type of interaction occurs when one organism kills and eats another. What type of interaction is that? predat ...
Secondary_4
... Sc6.1.2. Identify the different types of folds and conditions under which they form; Sc6.1.3. Define fractures and faults and explains how they are related to earthquakes; Sc6.1.4. Explain how mountains form and identify the associated plate boundaries; Sc6.1.5. Identify and explain Earthquakes; Sc ...
... Sc6.1.2. Identify the different types of folds and conditions under which they form; Sc6.1.3. Define fractures and faults and explains how they are related to earthquakes; Sc6.1.4. Explain how mountains form and identify the associated plate boundaries; Sc6.1.5. Identify and explain Earthquakes; Sc ...
6th_ELA_RC_2.3_CONNECT_MAIN_IDEAS_DW
... 1. Humans are responsible for causing the extinction of certain animals. 2. For example, poachers2 affect certain species by hunting animals for sport, food, and trade. 3. Humans also drive out animals and destroy their natural habitat. 4. Humans use land, where animals once lived, for farming and b ...
... 1. Humans are responsible for causing the extinction of certain animals. 2. For example, poachers2 affect certain species by hunting animals for sport, food, and trade. 3. Humans also drive out animals and destroy their natural habitat. 4. Humans use land, where animals once lived, for farming and b ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.