Part 2 - Mahopac Voyagers!
... D) Early Proterozoic Era D) lived on land ____21. Which event occurred at the start of the Mesozoic Era? ____17. From the study of fossils, what can be inferred about most species of plants and animals that have lived on the Earth? ...
... D) Early Proterozoic Era D) lived on land ____21. Which event occurred at the start of the Mesozoic Era? ____17. From the study of fossils, what can be inferred about most species of plants and animals that have lived on the Earth? ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... Result is a way to estimate divergence in species where the fossil record is missing ...
... Result is a way to estimate divergence in species where the fossil record is missing ...
DR Fossil Record
... 21. The periods when many species suddenly become extinct are called ______________________. 22. What are two of the events scientists think could have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs? _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...
... 21. The periods when many species suddenly become extinct are called ______________________. 22. What are two of the events scientists think could have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs? _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...
6-1 directed_reading_a 6-1 directed_reading_a
... 21. The periods when many species suddenly become extinct are called ______________________. 22. What are two of the events scientists think could have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs? _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...
... 21. The periods when many species suddenly become extinct are called ______________________. 22. What are two of the events scientists think could have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs? _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ...
Patterns of evolution
... Fossil Evidence of Mass Extinction Fossilization does not happen very often. Mass Extinctions also do not occur very ...
... Fossil Evidence of Mass Extinction Fossilization does not happen very often. Mass Extinctions also do not occur very ...
Chapter 26
... RNA could have been the template on which DNA was assembled DNA is much more stable and can be replicated more accurately so as genomes grew DNA grew ...
... RNA could have been the template on which DNA was assembled DNA is much more stable and can be replicated more accurately so as genomes grew DNA grew ...
Evolutionary Patterns
... Fossils: preserved remains or impressions left by organisms from the past 1. Allow us to calibrate phylogenies in terms of time 2. Provides a record of extinct species 3. Places evolutionary events in context with Earth’s history ...
... Fossils: preserved remains or impressions left by organisms from the past 1. Allow us to calibrate phylogenies in terms of time 2. Provides a record of extinct species 3. Places evolutionary events in context with Earth’s history ...
The History of Life
... At the end of the Mesozoic period, this single large mass of land began breaking apart resulting in a great divergence of many plant and animal species. ...
... At the end of the Mesozoic period, this single large mass of land began breaking apart resulting in a great divergence of many plant and animal species. ...
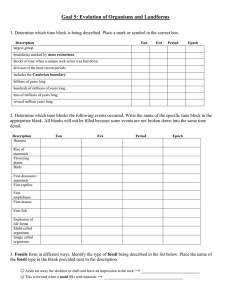
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... boundaries marked by mass extinctions blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down division of the most recent periods includes the Cambrian boundary billions of years long hundreds of millions of years long tens of millions of years long ...
... boundaries marked by mass extinctions blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down division of the most recent periods includes the Cambrian boundary billions of years long hundreds of millions of years long tens of millions of years long ...
File
... species produces more offspring that can survive; and the offspring with the most favorable traits are the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce ...
... species produces more offspring that can survive; and the offspring with the most favorable traits are the most likely to survive and pass on their genes. Fossils help us because they show us remains or imprints of once-living organisms. A group of organisms that can mate with each other to produce ...
The History of Life
... – Most organisms that ever lived on earth are now extinct – Modern organisms have unicellular (singlecelled) ancestors – Fossils occur in a particular order with older fossils in older rocks ...
... – Most organisms that ever lived on earth are now extinct – Modern organisms have unicellular (singlecelled) ancestors – Fossils occur in a particular order with older fossils in older rocks ...
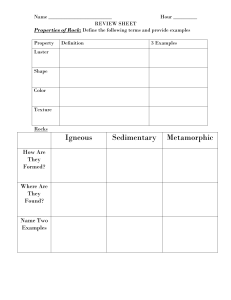
Key Vocabulary Terms
... F. The history of life found in fossils buried in the layers of the Earth. ...
... F. The history of life found in fossils buried in the layers of the Earth. ...
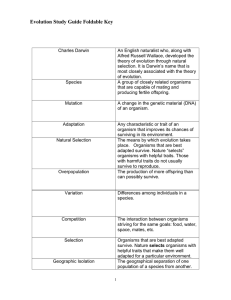
Charles Darwin
... theory of evolution through natural selection. It is Darwin’s name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. A group of closely related organisms that are capable of mating and ...
... theory of evolution through natural selection. It is Darwin’s name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. A group of closely related organisms that are capable of mating and ...
phenomena endosimbiosi – NICOLA GRUOSSO
... FOSSILS AND EVOLUTION – LAMKOUTAR ZACCARIA – 3A CUCINA The objectives of this presentation are: - understanding the relationship between the increasing oxygen in the atmosphere and life evolution; - showing examples of evolutionary convergence during the Jurassic period in the Tethys Sea; - using th ...
... FOSSILS AND EVOLUTION – LAMKOUTAR ZACCARIA – 3A CUCINA The objectives of this presentation are: - understanding the relationship between the increasing oxygen in the atmosphere and life evolution; - showing examples of evolutionary convergence during the Jurassic period in the Tethys Sea; - using th ...
Slide 1
... Non-Major’s Gen-Ed Biology Course Available for Fall 2011! Explore the diversity of life on Earth, along with the evolutionary relationships of organisms large and small. From bacteria to fungi, plants to animals, learn what makes each unique, and discover how they all interact …as well as the impac ...
... Non-Major’s Gen-Ed Biology Course Available for Fall 2011! Explore the diversity of life on Earth, along with the evolutionary relationships of organisms large and small. From bacteria to fungi, plants to animals, learn what makes each unique, and discover how they all interact …as well as the impac ...
Document
... (about 550 million years ago) when the variety of life forms explodes; billions of years long •Era: mass extinctions mark the boundaries between the eras; hundreds of millions years long •Period: blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down; tens of millions of years long •Epoch: divisions ...
... (about 550 million years ago) when the variety of life forms explodes; billions of years long •Era: mass extinctions mark the boundaries between the eras; hundreds of millions years long •Period: blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down; tens of millions of years long •Epoch: divisions ...
The history of life on earth
... Fossil record is the sequence in which fossils occur in undisturbed sedimentary rock. Fossil record is imcomplete because most fossils are remains of organisms with hard shells or bony skeleton. ...
... Fossil record is the sequence in which fossils occur in undisturbed sedimentary rock. Fossil record is imcomplete because most fossils are remains of organisms with hard shells or bony skeleton. ...
Read more about Kidwell`s work
... have been found—but scientists are now learning how to make best use of that incomplete history. Kidwell has combined geological fieldwork, experiments in the lab and measurements in modern environments to investigate how the fossil record is formed and how to best use it to understand the past and ...
... have been found—but scientists are now learning how to make best use of that incomplete history. Kidwell has combined geological fieldwork, experiments in the lab and measurements in modern environments to investigate how the fossil record is formed and how to best use it to understand the past and ...
GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE
... Major group of organisms becomes extinct new time interval (66 million years age = end of the Mesozoic Era or beginning of the Cenozoic Era) Dinosuars became extinct (no more fossils) ...
... Major group of organisms becomes extinct new time interval (66 million years age = end of the Mesozoic Era or beginning of the Cenozoic Era) Dinosuars became extinct (no more fossils) ...
Evolution of Life and Mass Extinctions
... western NYS because old oceans that covered the state evaporated during the hot and dry Silurian Period (noted on reference tables) ...
... western NYS because old oceans that covered the state evaporated during the hot and dry Silurian Period (noted on reference tables) ...
Evidence for Evolution - Mr. Blankenship's pages
... Indicator 5.5 Exemplify scientific evidence in the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology that underlies the theory of biological evolution. ...
... Indicator 5.5 Exemplify scientific evidence in the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology that underlies the theory of biological evolution. ...
chapter 16 section 4 notes
... • Nucleic acids- comparing nucleotide sequences also shows how long it has been since two species _______________ • Together proteins and nucleic acids support the fossil record ...
... • Nucleic acids- comparing nucleotide sequences also shows how long it has been since two species _______________ • Together proteins and nucleic acids support the fossil record ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.