* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Charles Darwin
Dawkins vs. Gould wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness in humans wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
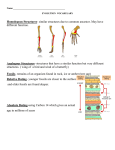
Evolution Study Guide Foldable Key Charles Darwin An English naturalist who, along with Alfred Russell Wallace, developed the theory of evolution through natural selection. It is Darwin’s name that is most closely associated with the theory of evolution. A group of closely related organisms that are capable of mating and producing fertile offspring. Species Mutation A change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism. Adaptation Any characteristic or trait of an organism that improves its chances of surviving in its environment. The means by which evolution takes place. Organisms that are best adapted survive. Nature “selects” organisms with helpful traits. Those with harmful traits do not usually survive to reproduce. The production of more offspring than can possibly survive. Natural Selection Overpopulation Variation Differences among individuals in a species. Competition The interaction between organisms striving for the same goals: food, water, space, mates, etc. Selection Organisms that are best adapted survive. Nature selects organisms with helpful traits that make them well adapted for a particular environment. The geographical separation of one population of a species from another. Geographic Isolation 1 Fossil The preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Sedimentary Rock Rock formed by the laying down of sediments – particles of sand and rock carried most often by water. Dating Methods Ways to estimate the age of fossils Relative Dating Reading the layers of sediment to determine the oldest and youngest fossils. The oldest fossils are usually in the bottom layer; the youngest in the upper layers. Determining the amount of radioactive elements that are present in a fossil. The amount that is left in the rock tells scientists how old the fossil is. Organisms that no longer live on Earth. Absolute Dating Extinct Organisms Fossil Record The millions of fossils that scientists have collected. Geologic Time Scale A chart of calendar that shows when the major groups of organisms lived over the Earth’s 4.6 billion year history. Evolution A change in a species over time through natural selection. Gradualism Evolution that takes place gradually over time. Punctuated Equilibrium Evolution that takes place rapidly especially as a result of a catastrophic environmental event. 2 Ways to show evolutionary relationships Homologous Structures Body structure Development before birth (embryology) DNA sequences Structures that are similar in form but different in use such as the flipper of a whale and the wing of a bird. Branching Tree A diagram that shows how different groups of organisms are related. 3